LPS8N -- LoRaWAN Gateway User Manual

Table of Contents:
- 1. Introduction
- 2. Access and Configure LPS8N
- 3. Typical Network Setup
- 4. Example: Configure as a LoRaWAN gateway
- 5. Web Configure Pages
- 6. More features
- 6.1 NTP Service/Time Synchronization
- 6.2 Packet Filtering
- 6.3 Remote Access
- 6.4 How to decode ABP LoRaWAN node
- 6.5 How to set data to MQTT broker
- 6.6 How the gateway connects to Chirpstack v3/v4 via gateway-bridge
- 6.7 How does the gateway connect to Chirpstack via MQTT Forwarder
- 6.8 How to extend the gateway size of memory with USB device (SD/TF card, USB flash drive).
- 6.9 More instructions
- 6.10 Auto-Provision
- 7. Linux System
- 8. Upgrade Linux Firmware
- 9. OTA System Update
- 10. FAQ
- 11. Trouble Shooting
- 11.1 I get kernel error when install new package, how to fix?
- 11.2 How to recover the LPS8N if the firmware crashes
- 11.3 I configured LPS8N for WiFi access and lost its IP. What to do now?
- 11.4 I connect to the LPS8N's SSID but LPS8N didn't assign DHCP IP to my laptop?
- 11.5 When i power on LPS8N , i can only see PWR LED is on. other LEDs are not blinking.
- 11.6 Why does the gateway reboot every 15 minutes without Internet?
- 12. Order Info
- 13. Packing Info
- 14. Support
1. Introduction
1.1 What is the LPS8N
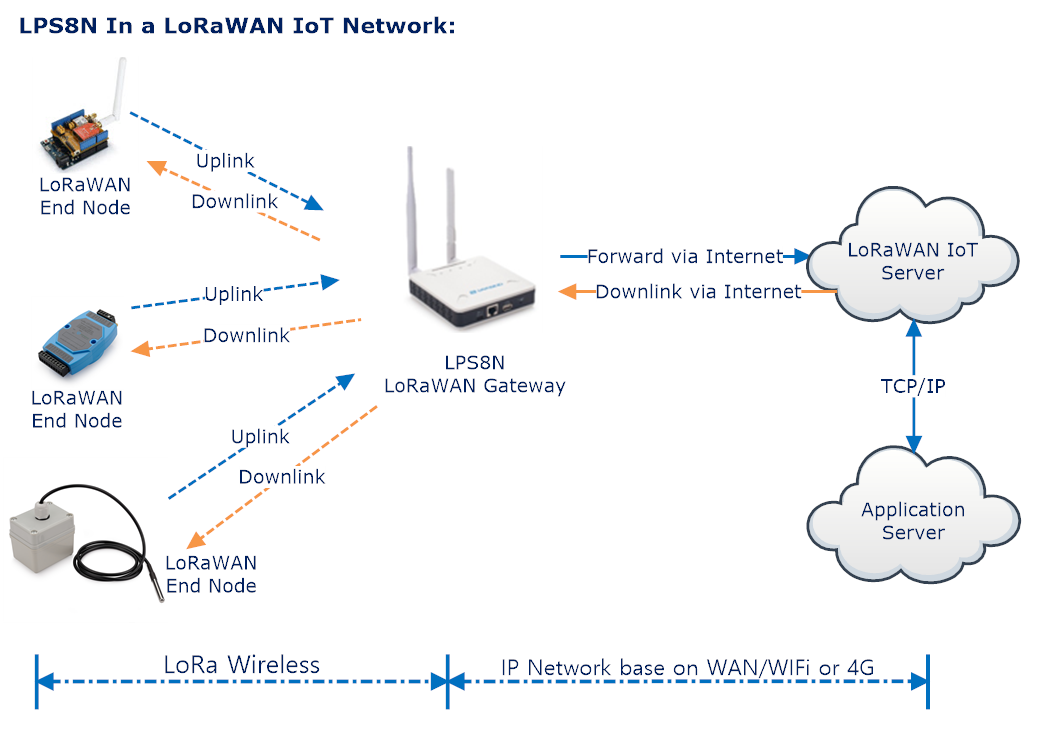
The LPS8N is an open source LoRaWAN Indoor Gateway. It lets you bridge LoRa wireless network to an IP network via WiFi, Ethernet, 3G or 4G cellular network. The LoRa wireless allows users to send data and reach extremely long ranges at low data-rates.
The LPS8N uses Semtech packet forwarder & LoRaWAN Station connection and fully compatible with LoRaWAN protocol. It includes a SX1302 LoRaWAN concentrator, which provides 10 programmable parallel demodulation paths.
LPS8N has pre-configured standard LoRaWAN frequency bands to use for different countries. User can also customized the frequency bands to use in their own LoRa network.
LPS8N can communicate with ABP LoRaWAN end node without LoRaWAN server. System integrator can use it to integrate with their existing IoT Service without set up own LoRaWAN server or use 3rd party LoRaWAN service.
1.2 Specifications
Hardware System:
Linux Part:
- 400Mhz ar9331 processor
- 64MB RAM
- 16MB Flash
Interface:
- 10M/100M RJ45 Ports x 1
- WiFi : 802.11 b/g/n
- LoRaWAN Wireless
- Power Input: 5V DC, 2A, Type C
- USB 2.0 host connector x 1
- Mini-PCI E connector x 1
- SX1302 + 2 x SX1250
- 802.3af PoE (for LPS8NP version)
WiFi Spec:
- IEEE 802.11 b/g/n
- Frequency Band: 2.4 ~ 2.462GHz
- Tx power:
- 11n tx power : mcs7/15: 11db mcs0 : 17db
- 11b tx power: 18db
- 11g 54M tx power: 12db
- 11g 6M tx power: 18db
- Wifi Sensitivity
- 11g 54M : -71dbm
- 11n 20M : -67dbm
LoRa Spec:
- Up to -140 dBm sensitivity
- 70 dB CW interferer rejection at 1 MHz offset
- Able to operate with negative SNR, CCR up to 9dB
- 8 x 8 channels LoRa packet detectors,8 x SF5-SF12 LoRa demodulators,8 x SF5-SF10 LoRa demodulators,125/250/500 kHz LoRa demodulator and 1 x (G)FSK demodulator
- Dual digital TX & RX radio front-end interfaces
- 10 programmable parallel demodulation paths
- Dynamic data-rate (DDR) adaptation
- True antenna diversity or simultaneous dual-band operation
Cellular 4G LTE (optional):
- Quectel EC25 LTE module
- Micro SIM Slot
- External 4G Sticker Antenna.
- Up to 150Mbps downlink and 50Mbps uplink data rates
- Worldwide LTE,UMTS/HSPA+ and GSM/GPRS/EDGE coverage
- MIMO technology meets demands for data rate and link reliability in modem wireless communication systems
1.3 Features
- Open Source OpenWrt system
- Managed by Web GUI, SSH via WAN or WiFi
- Remote access with Reverse-SSH or remote.it
- Emulates 49x LoRa demodulators
- LoRaWAN Gateway
- 10 programmable parallel demodulation paths
- Pre-configure to support different LoRaWAN regional settings.
- Allow to customize LoRaWAN regional parameters.
- Support Local decode ABP end node info and transfer to MQTT server
- Support different level log in.
- Support Semtech Packet Forwarder
- Support LoRaWAN basic station.
- Optional 3G/4G cellular connection
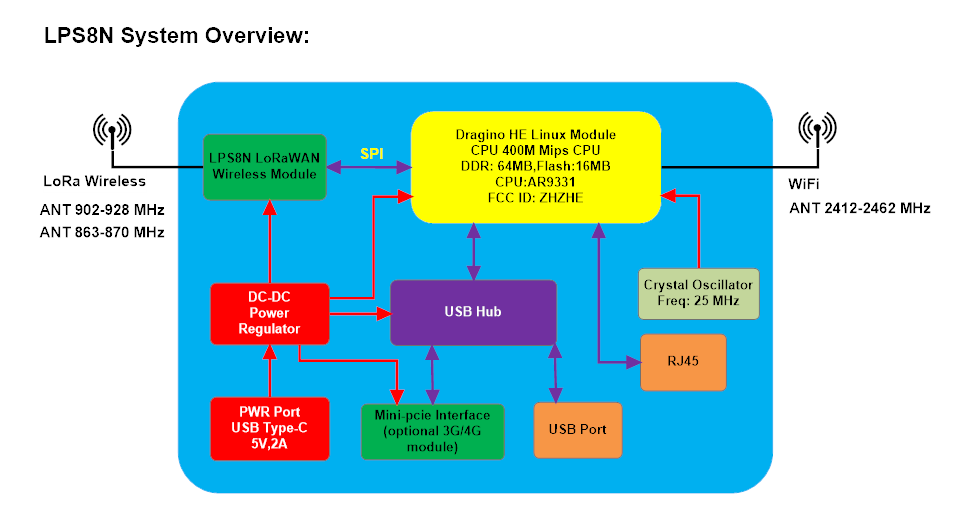
1.4 Hardware System Structure
1.5 LPS8N Applications
1.6 LED Indicators
LPS8N has totally four LEDs, They are:
- Power LED
 : This RED LED will be solid on if the device is properly powered.
: This RED LED will be solid on if the device is properly powered. - Wireless LED
 : This GREEN LED will be solid on if the device enablel WiFi AP.
: This GREEN LED will be solid on if the device enablel WiFi AP. - SYS LED
 : This RGB LED will shows different colors on different state:
: This RGB LED will shows different colors on different state:- SOLID BLUE: Device is alive with LoRaWAN server connection.
- BLINKING BLUE: a) Device has internet connection but no LoRaWAN Connection. or b) Device is in booting stage, in this stage, it will BLINKING BLUE for several seconds and then with SOLID RED and BLINKING BLUE together
- SOLID RED: Device doesn't have Internet connection.
- ETH LED
 : This LED shows the ETH interface connection status.
: This LED shows the ETH interface connection status.
1.7 Button Instruction
LPS8N has a black toggle button, which is:
➢ Long press 4-5s: the gateway will reload the Network and Initialize wifi configuration
LED status: SYS LED will BLINKING BLUE Until the reload is finished.
➢ Long press more than 30s: the gateway will restart and restore factory settings.
LED status: When the user releases the button, the LED will TURN OFF.
2. Access and Configure LPS8N
The LPS8N is configured as a WiFi Access Point by factory default. You can access and configure the LPS8N after connecting to its WiFi network, or via its WAN Ethernet port.
2.1 Find IP address of LPS8N
2.1.1 Connect via WiFi

At the first boot of LPS8N, it will auto generate a WiFi network called dragino-xxxxxx with password: dragino+dragino
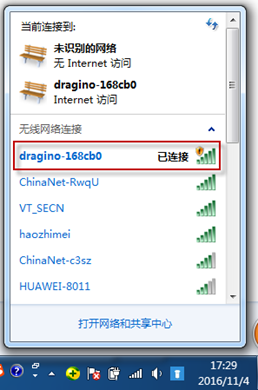
User can use a PC to connect to this WiFi network. The PC will get an IP address 10.130.1.xxx and the LPS8N has the default IP 10.130.1.1
2.1.2 Connect via Ethernet with DHCP IP from router
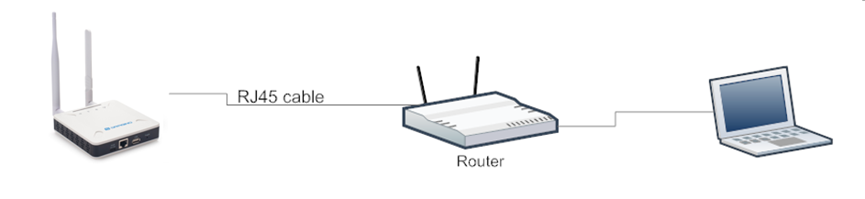
Alternatively, connect the LPS8N Ethernet port to your router and LPS8N will obtain an IP address from your router. In the router's management portal, you should be able to find what IP address the router has assigned to the LPS8N. You can also use this IP to connect.
2.1.3 Connect via WiFi with DHCP IP from router
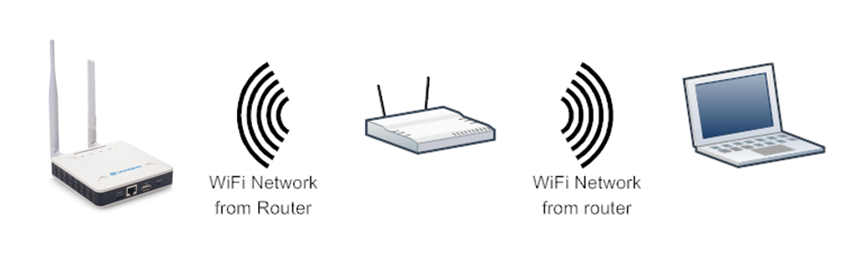
If the LPS8N already connect to the router via WiFi, use can use the WiFi IP to connect to LPS8N.
2.1.4 Connect via Ethernet with fall back ip
The WAN port also has a fall back ip address for access if user doesn't connect to uplink router. Click here to see how to configure.
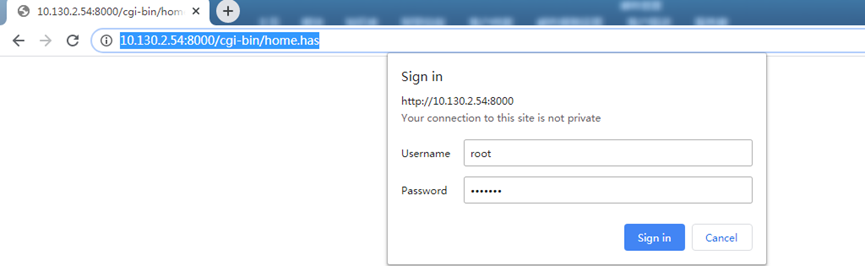
2.2 Access Configure Web UI
Web Interface
Open a browser on the PC and type the LPS8N ip address (depends on your connect method)
http://10.130.1.1/ (Access via WiFi AP network)
or
http://IP_ADDRESS or http:// IP_ADDRESS:8000
You will see the login interface of LPS8N as shown below.
The account details for Web Login are:
User Name: root
Password: dragino
3. Typical Network Setup
3.1 Overview
The LPS8N supports flexible network set up for different environments. This section describes the typical network topology. The network set up includes:
- WAN Port Internet Mode
- WiFi Client Mode
- WiFi AP Mode
3.2 Use WAN port to access Internet
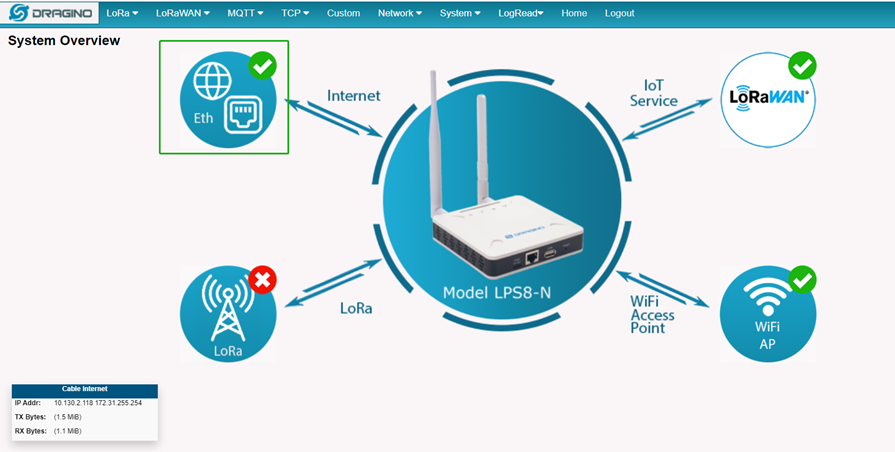
By default, the LPS8N is set to use the WAN port to connect to an upstream network. When you connect the LPS8N's WAN port to an upstream router, LPS8N will get an IP address from the router and have Internet access via the upstream router. The network status can be checked in the home page:
3.3 Access the Internet as a WiFi Client
In the WiFi Client Mode, LPS8N acts as a WiFi client and gets DHCP from an upstream router via WiFi.
The settings for WiFi Client is under page System--> WiFi --> WiFi WAN Client Settings
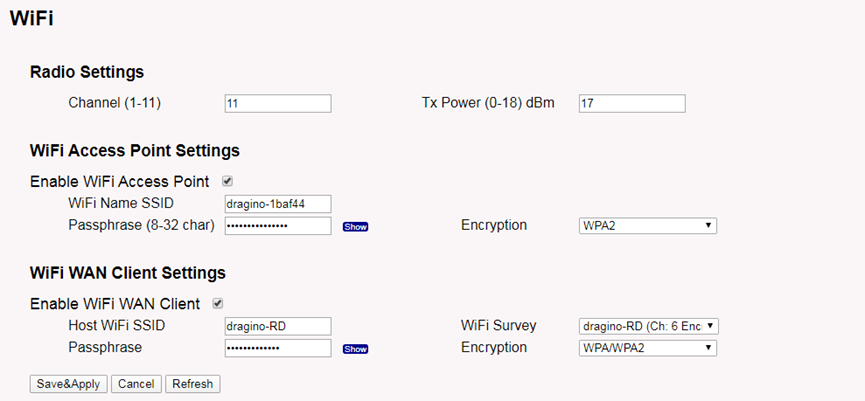
In the WiFi Survey Choose the WiFi AP, and input the Passphrase then click Save & Apply to connect.
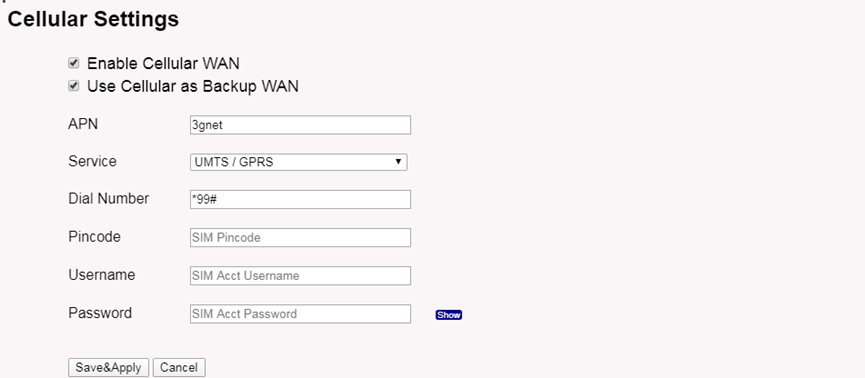
3.4 Use built-in 4G modem for internet access
If the LPS8N has 3G/4G Cellular modem, user can use it as main internet connection or back up.
First, install the Micro SIM card as below direction
Second, Power off/ ON LPS8N to let it detect the SIM card.

The set up page is System --> Cellular
While use the cellular as Backup WAN, device will use Cellular for internet connection while WAN port or WiFi is not valid and switch back to WAN port or WiFi after they recover.
When cellular fails to connect or has problems, users can refer to this link to Trouble Shooting:How to Trouble Shooting if Cellular connection fails
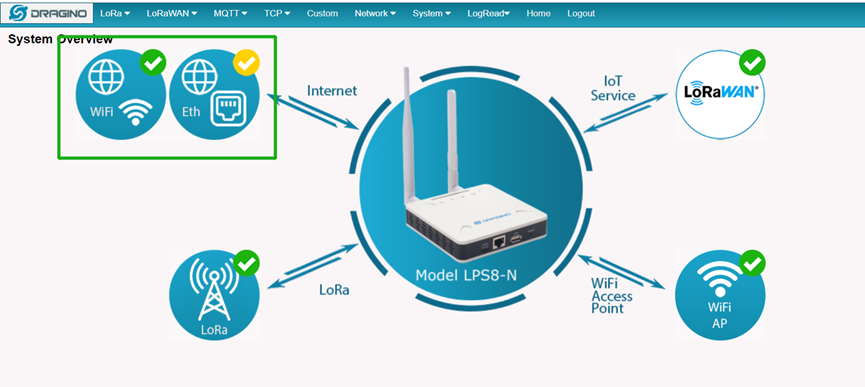
3.5 Check Internet connection
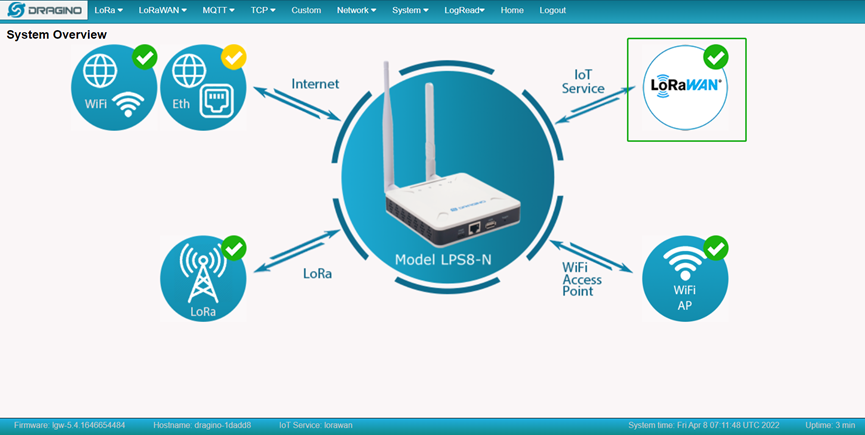
In the home page, we can check the Internet connection.
- GREEN Tick
 : This interface has Internet connection.
: This interface has Internet connection. - Yellow Tick
 : This interface has IP address but don't use it for internet connection.
: This interface has IP address but don't use it for internet connection. - RED Cross
 : This interface doesn't connected.
: This interface doesn't connected.
4. Example: Configure as a LoRaWAN gateway
LPS8N is fully compatible with LoRaWAN protocol. It uses the legacy Semtech Packet forwarder to forward the LoRaWAN packets to server. The structure is as below.

This chapter describes how to use the LPS8N to work with (TTN v3) LoRaWAN Server (www.thethingsnetwork.org)
4.1 Create a gateway in TTN V3 Server
Step 1: Get a Unique gateway ID.
Every LPS8N has a unique gateway id. The ID can be found at LoRaWAN page:
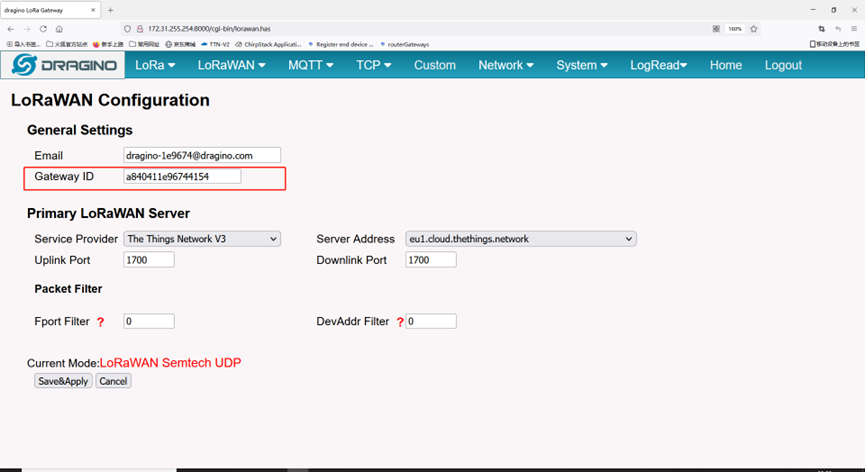
The example gateway id is: a840411e96744154
Step 2: Sign up a user account in TTN server
https://account.thethingsnetwork.org/register
Step 3: Choose the TTNv3 Cluster Picker
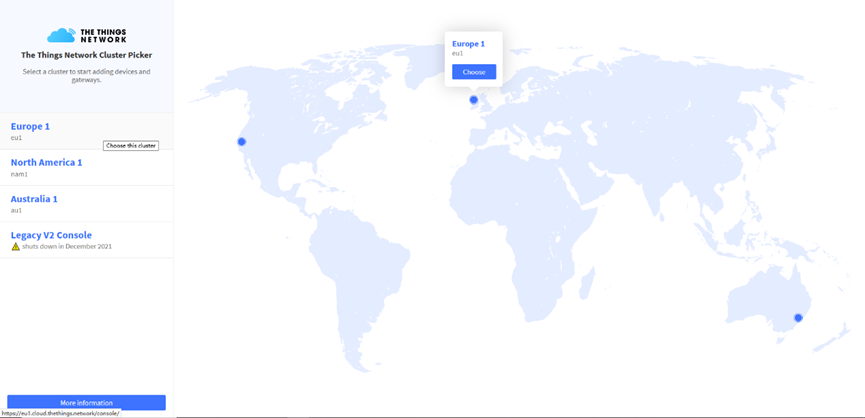
Note: Choose the cluster corresponds to a specific Gateway server address
- Europe 1 corresponding Gateway server address: eu1.cloud.thethings.network
- North America 1 corresponding Gateway server address: nam1.cloud.thethings.network
- Australia 1 corresponding Gateway server address: au1.cloud.thethings.network
- Legacy V2 Console : TTN v2 shuts down in December 2021
Step 4: Create a Gateway
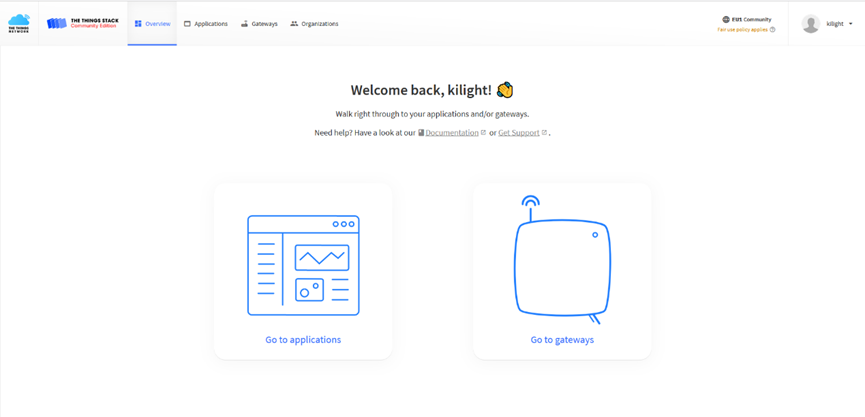
Click the Gateway icon and then click Add gateway.
Open the following page:
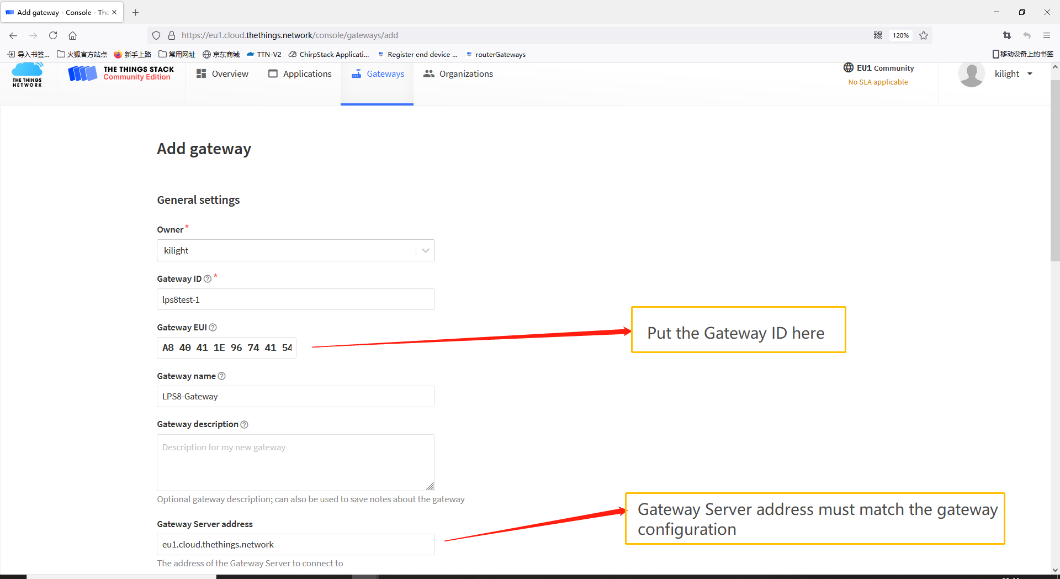
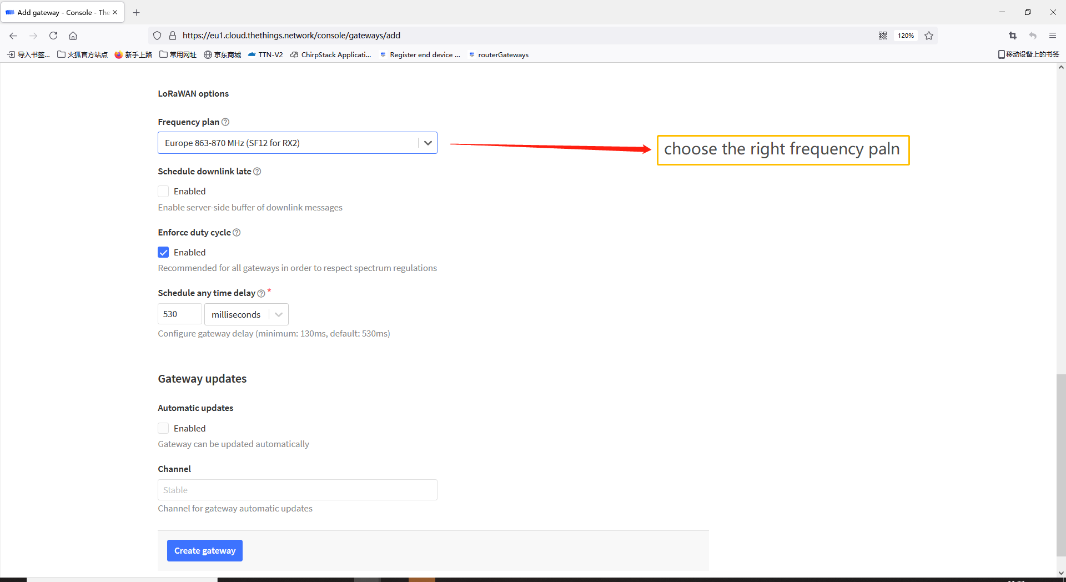
Notice: Gateway Server address must match the gateway configuration, otherwise you will have problem for End Node to join the network.
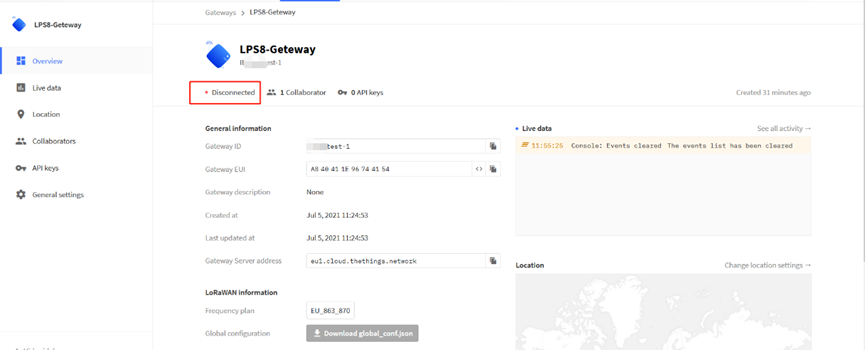
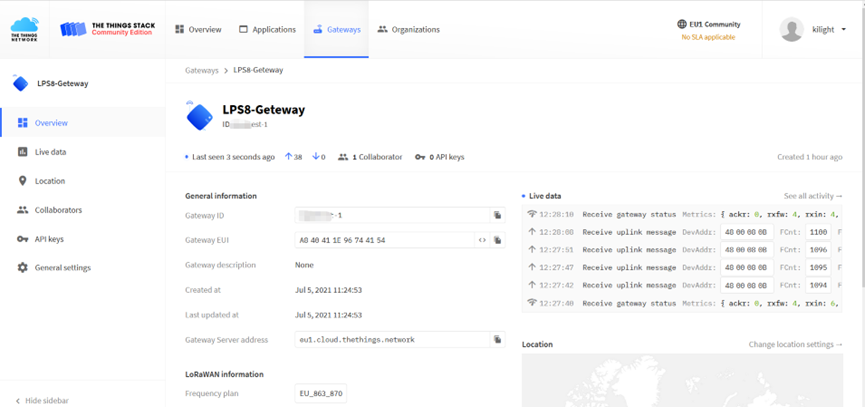
After creating the gateway, you can see the gateway info, as below.
4.2 Configure LPS8N to connect to TTN v3
You can now configure the LPS8N to let it connect to TTN network V3.
Make sure your LPS8N has a working Internet Connection first.
Choose the right server provider and click Save&Apply.
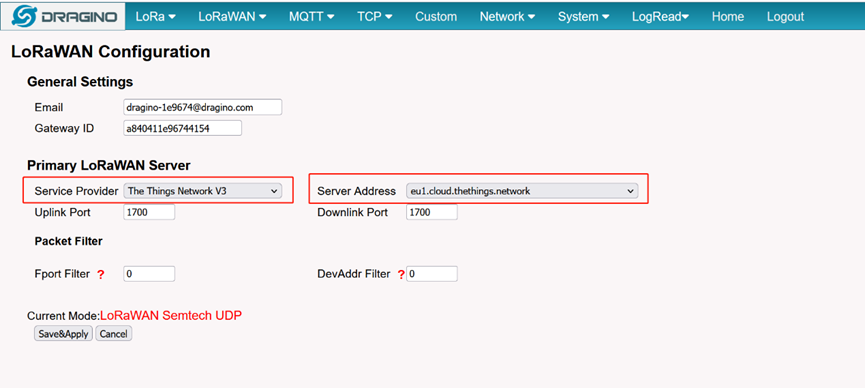
Note: The server address must match the Gateway server address you choose in TTN V3.
In the home page, we can see the LoRaWAN connection is ready now.
In TTN v3 portal, we can also see the gateway is connected.
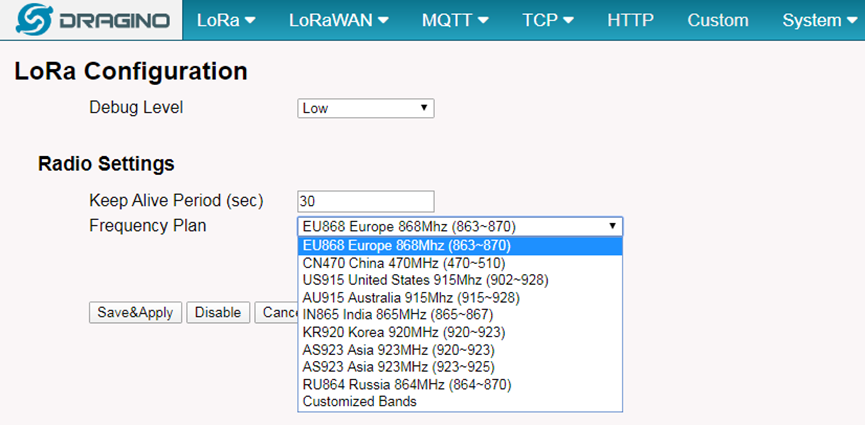
4.3 Configure frequency
We also need to set the frequency plan in LPS8N to match the end node we use, so to receive the LoRaWAN packets from the LoRaWAN sensor.
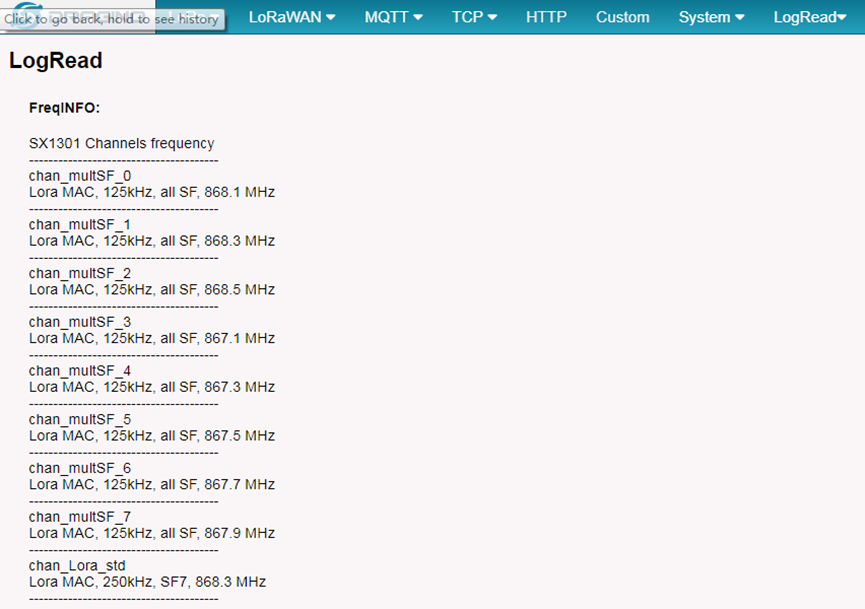
In logread page, user can check the frequency actually used.
4.4 Add a LoRaWAN End Device
This section shows how to add a LoRaWAN End device to a LoRaWAN network and see the data from TTN web site.
We use LT-22222-L IO Controller as a reference device - the setup for other LoRaWAN devices will be similar.

Step 1: Create a Device definition in TTN v3 with the OTAA keys from the example LT-22222-L IO Controller device.
Three codes are required to define the device in TTN v3:
- DEV EUI - Unique ID code for a particular device.
- APP EUI - ID code for an Application defined in TTN v3.
- APP Key - Unique key to secure communications with a particular device.
A set of these codes are stored in each device by the manufacturer as the default codes for that particular device. Each device is shipped with a sticker with the default Device EUI as shown below.

Note: You may be able to change these codes in a device by using a configuration facility on the device e.g. the LT-22222 uses a serial port access and a series of AT commands. Changing the codes may be necessary in the case where you have to use codes assigned by a LoRa WAN server.
For the TTN v3 server, you can use the codes set in the device as in the following example.
Select Add Application to open the screen below.
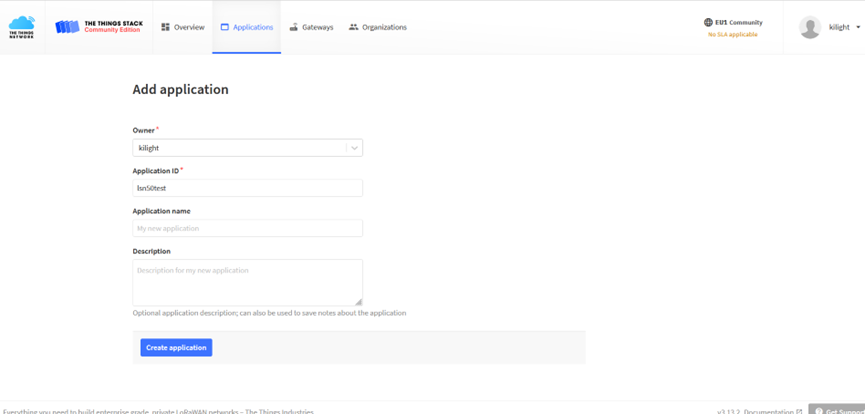
Open the Application select Add end device
Start Register the end device
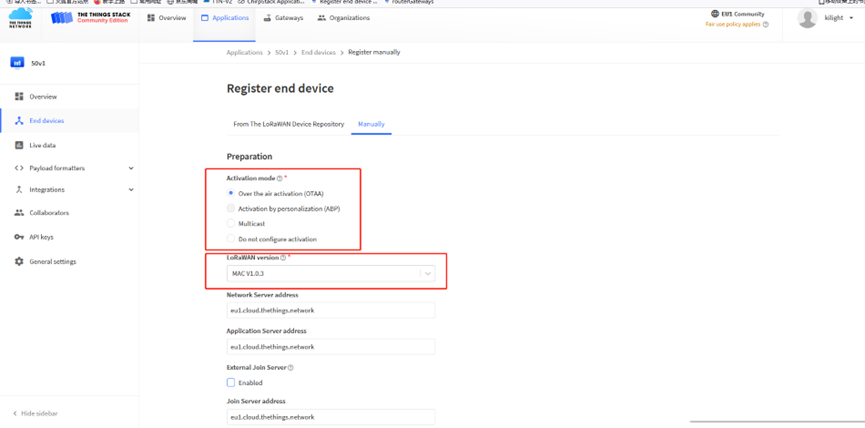
Select OTAA activation mode
The LoRaWAN version for your device should be provided by the manufacturer in a datasheet as LoRaWAN version or LoRaWAN specification. The most commonly used LoRaWAN versions are v1.0.2 and v1.0.3.
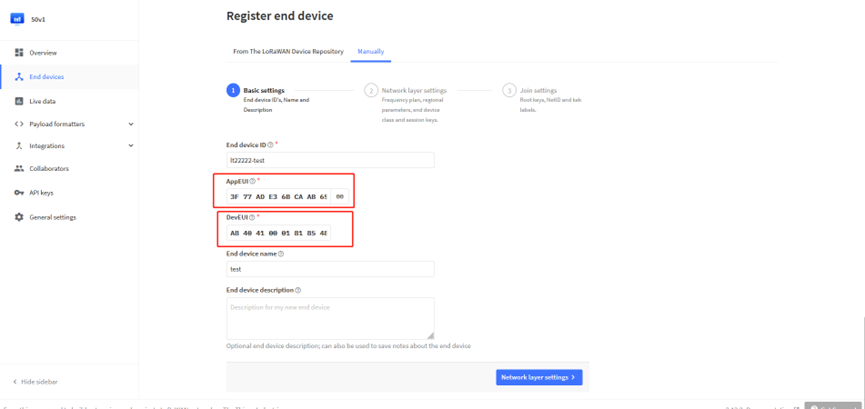
First, input the End device ID, AppEUI and DevEUI.
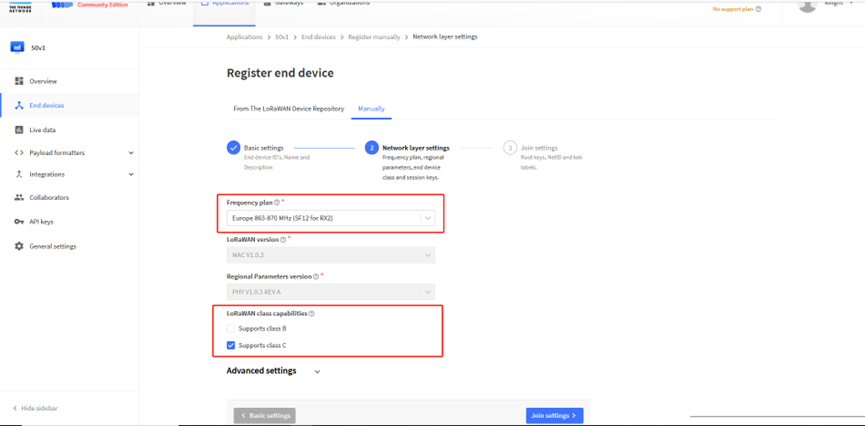
Secondly, choose the corresponding frequency and LoRaWAN class capabilities.
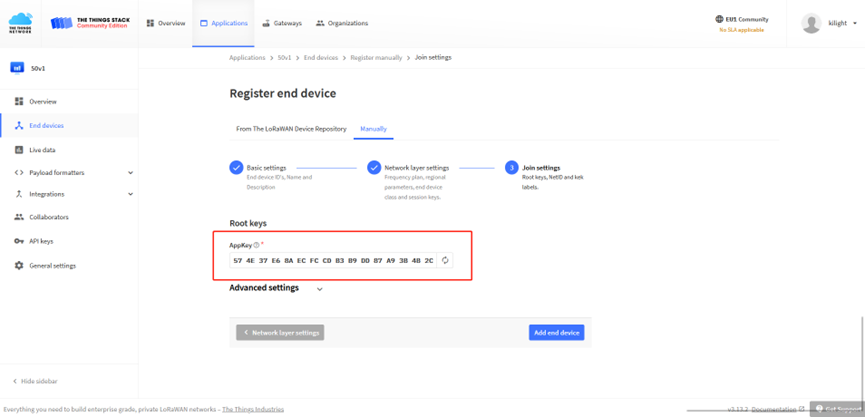
Finally, Application layer settings input the corresponding AppKey. Before saving the configuration, check that the data matches the device.
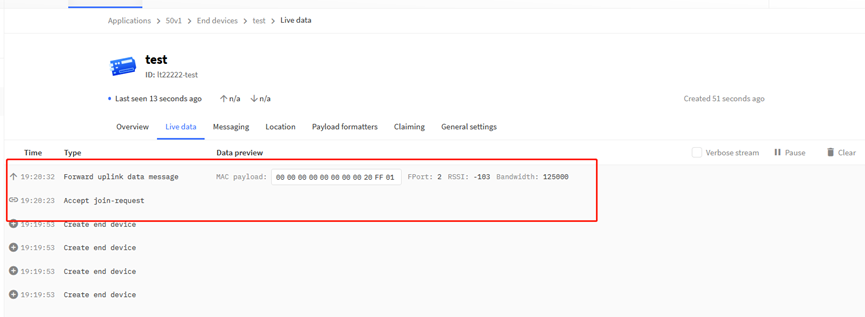
Step 2: Power on LT-22222-L device and it will automatically join the TTN network. After joining successfully, it will start to upload messages to the TTN v3. Select the Live data tab and you will see the data appearing in the panel.
Note that it may take some time for the device data to appear in the TTN v3 display.
5. Web Configure Pages
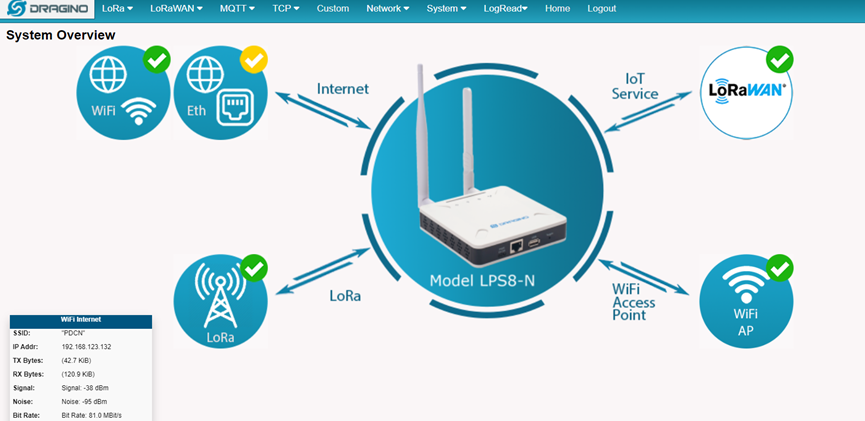
5.1 Home
Shows the system running status.
5.2 LoRa Settings
5.2.1 LoRa --> LoRa
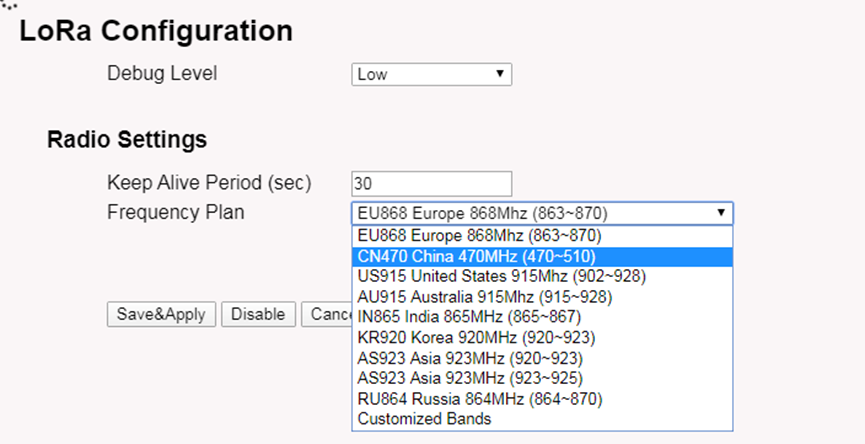
This page shows the LoRa Radio Settings. There are a set of default frequency band according to LoRaWAN protocol, and user can customized the band* as well.
Different LPS8N hardware version can support different frequency range:
- 868: valid frequency: 863Mhz ~ 870Mhz. for bands EU868, RU864, IN865 or KZ865.
- 915: valid frequency: 902Mhz ~ 928Mhz. for bands US915, AU915, AS923 or KR920
After user choose the frequency plan, he can see the actually frequency in used by checking the page LogRead --> LoRa Log
Note *: See this instruction for how to customize frequency band
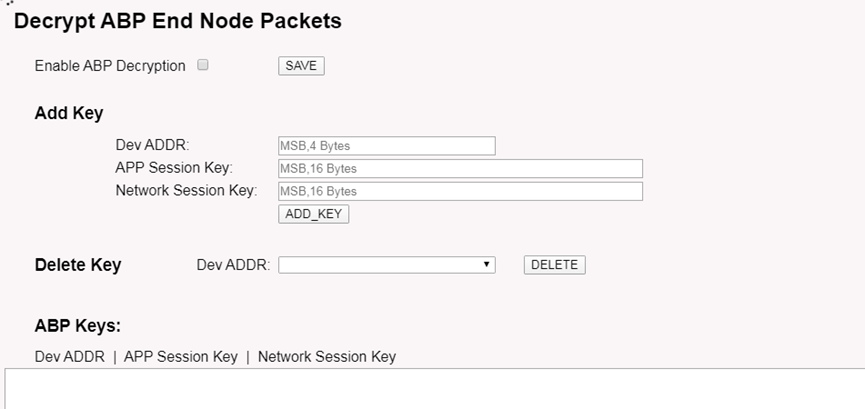
5.2.2 LoRa --> ABP Decryption
The LPS8N can communicate with LoRaWAN ABP End Node without the need of LoRaWAN server. It can be used in some cases such as:
- No internet connection.
- User wants to get data forward in gateway and forward to their server based on MQTT/HTTP, etc. (Combine ABP communication method and MQTT forward together).
Detail of this feature: Communication with ABP End Node
5.3 LoRaWAN Settings
5.3.1 LoRaWAN --> LoRaWAN
This page is for the connection set up to a general LoRaWAN Network server such as: TTN, ChirpStack etc.
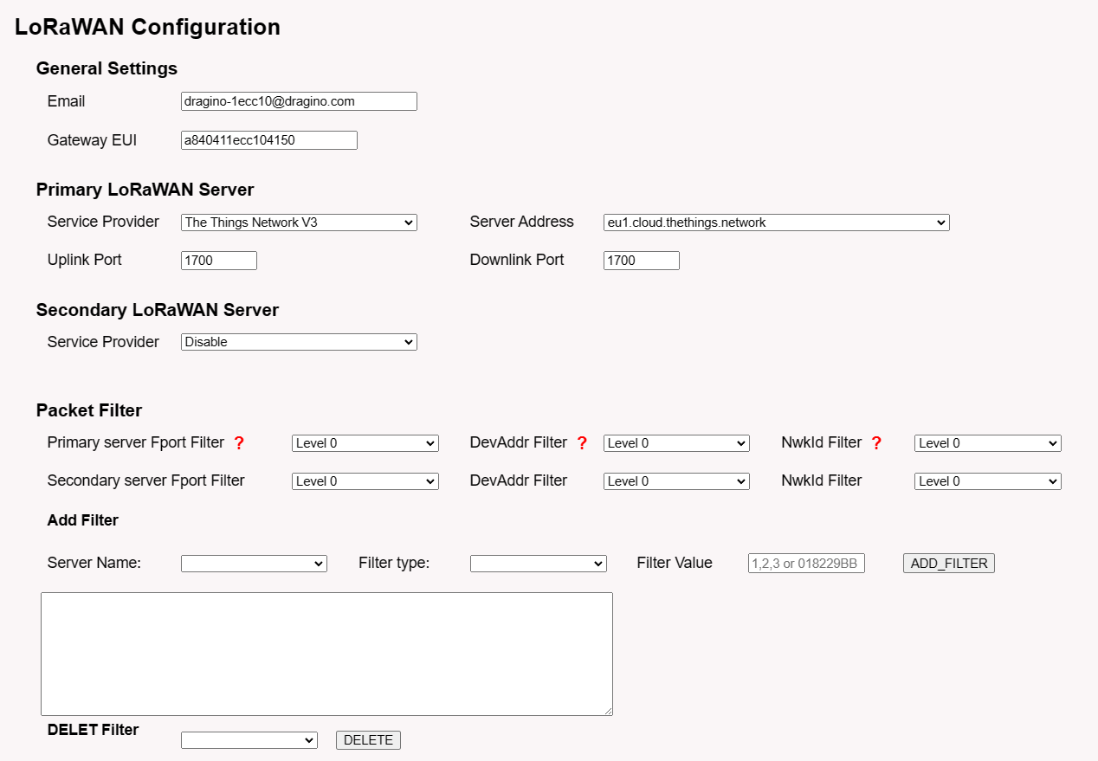
Note:
*: User can ignore the latitude and longitude settings here, LPS8N will use the actually value from GPS module.
**: Packet filter is to drop the unwanted LoRaWAN packet, instruction see here:
See: Filter unwanted LoRaWAN packets
5.3.2 LoRaWAN --> LoRaWAN -- Basic Station
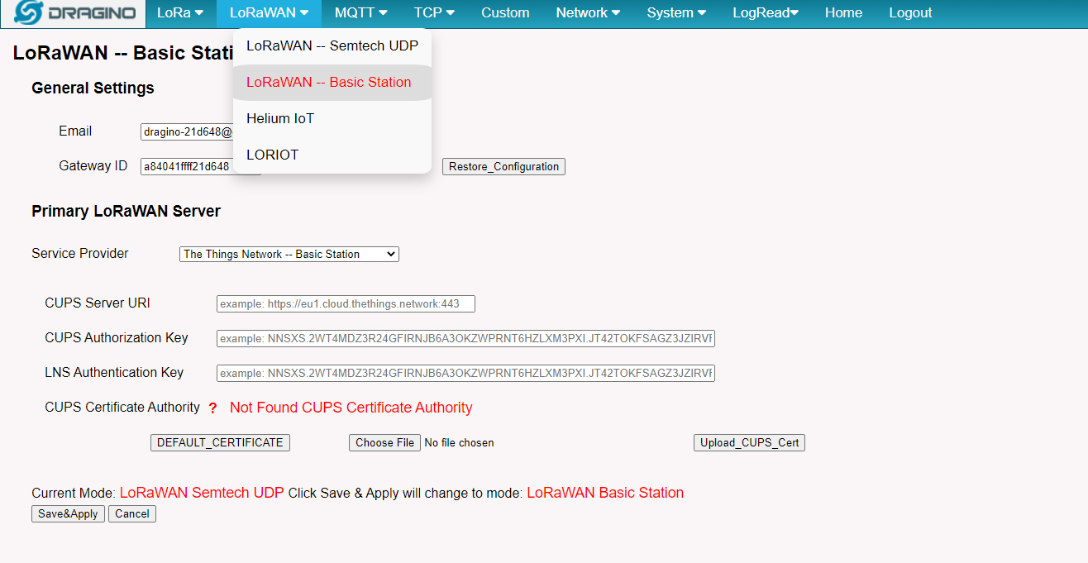
Please see this instruction to know more detail and a demo of how to connect to AWS-IoT LoRaWAN Core.
The basic station mode support TTN/AWS/Chirpstack/ThingPark/Senet Platform.
Instruction:
ThingPark
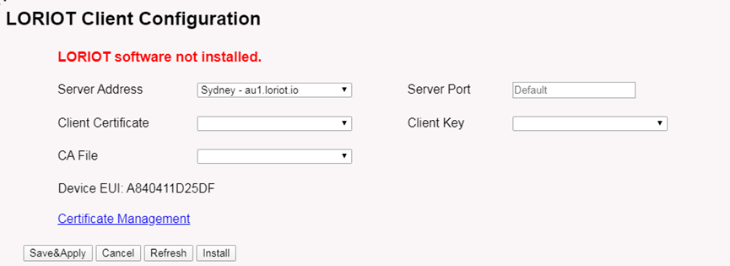
5.3.3 LoRaWAN --> LORIOT
Settings to communicate to LORIOT LoRaWAN Network Server: https://www.loriot.io/
Instruction: Notes for LORIOT
5.4 MQTT Settings
If end nodes works in ABP mode, user can configure LPS8N to transfer the data to MQTT broker,
Instruction: MQTT Forward Instruction
5.5 Network
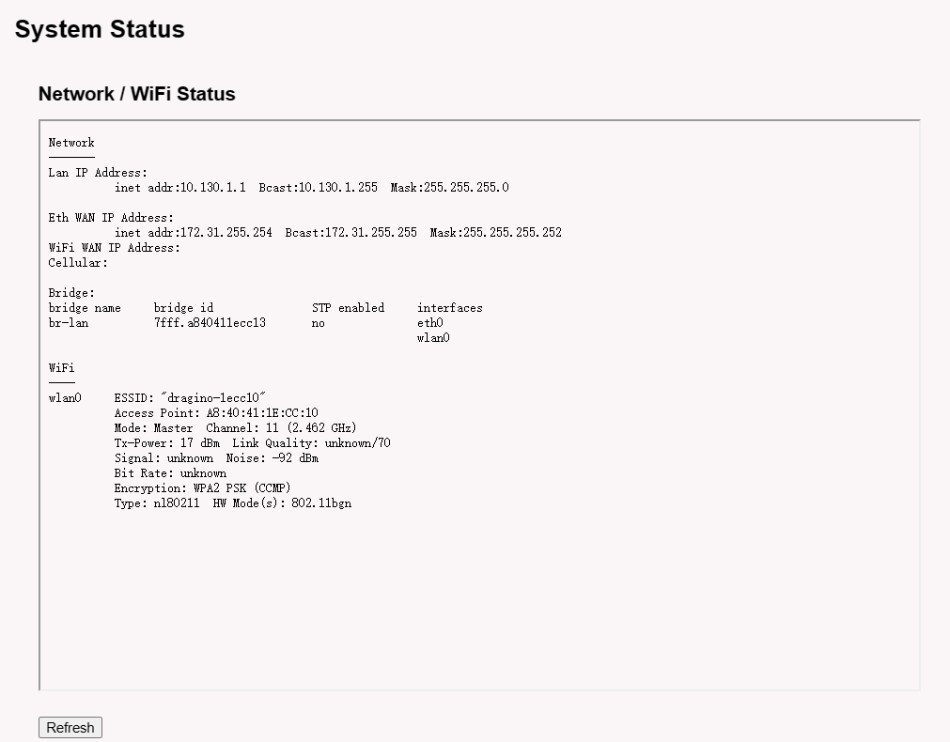
5.5.1 Network --> Network Status
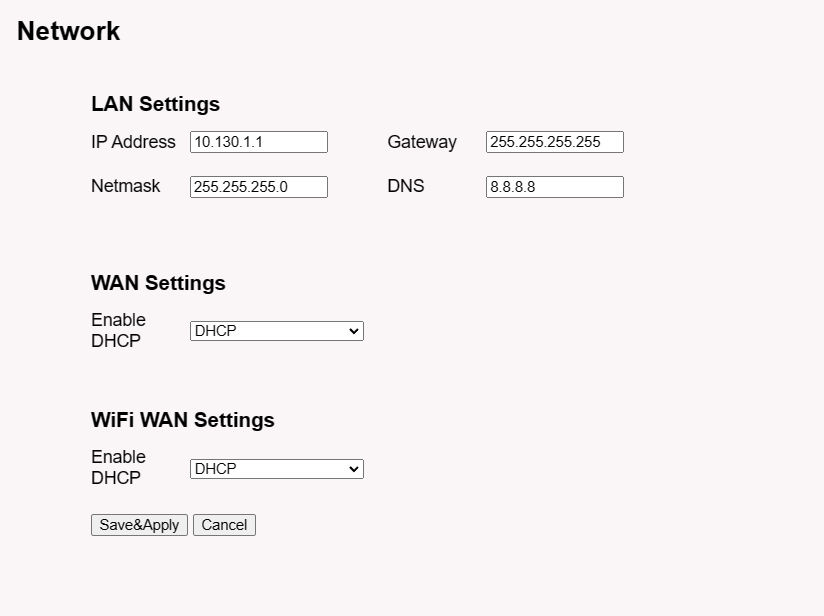
5.5.2 Network --> Network
LAN Settings: When the LPS8N has the AP enable, LAN settings specify the network info for LPS8N's own network.
WAN Settings: Setting for LPS8N WAN port
WiFi Settings: Setting for LPS8N WiFi IP when use it as WiFi Client
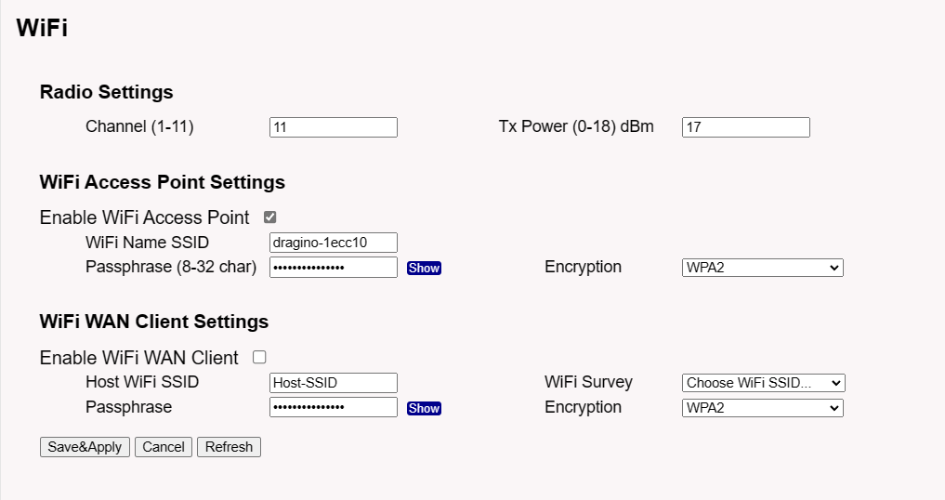
5.5.3 Network --> WiFi
LPS8N WiFi Settings.
5.5.4 Network --> Cellular
While use the cellular as Backup WAN, device will use Cellular for internet connection while WAN port or WiFi is not valid and switch back to WAN port or WiFi after they recover.
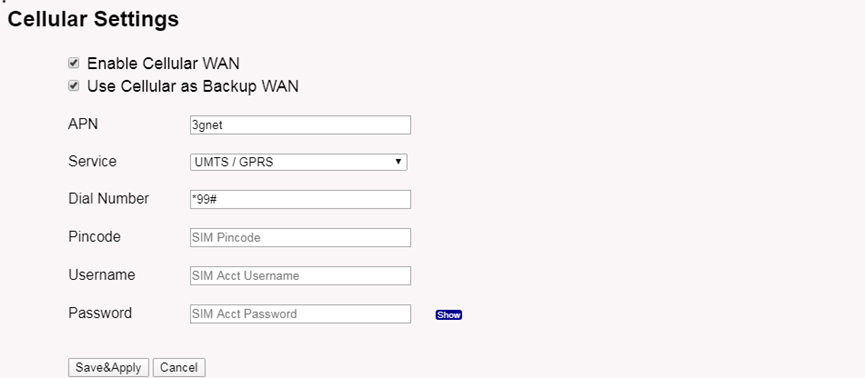
Note *: For LPS8N which doesn't have the cellular module, this page will shows Cellular not detected.
When cellular fails to connect or has problems, users can refer to this link to Trouble Shooting:How to Trouble Shooting if Cellular connection fails
5.6 System
5.6.1 System --> System Overview
Shows the system info:
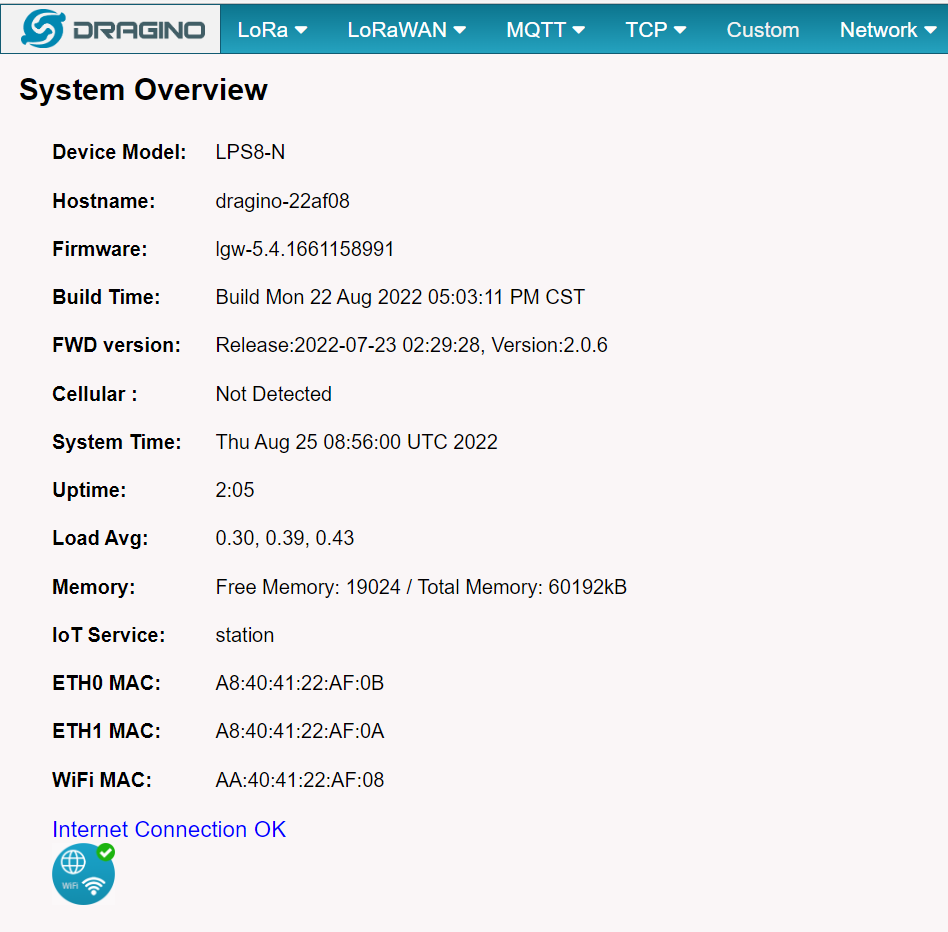
5.6.2 System --> General ( login settings)

System Password:
There are two login for LPS8N: root /dragino or admin /dragino. Both root and admin has the same right for WEB access. But root user has also the right to access via SSH to Linux system. admin only able to access WEB interface.
This page can be used to set the password for them.
Timezone: Set device timezone.
Port forwarding: Enable/Disable the HTTP and SSH access via WAN interface.
Fallback Settings: Enable/Disable the Fallback interface.
Keepalive_Script: Set the keepalive_scrpt interval.
Logread Level: Change the logread level.
Internet Detect and Recover:
Auto Detect: Internet Detect is enabled by default. When there is no gateway network, it will reboot after 15 minutes.
Manual Detect: In Manual Detect, User can choose wifi, ethernet, 4g or disable detect
5.6.3 System --> Backup/Restore Config
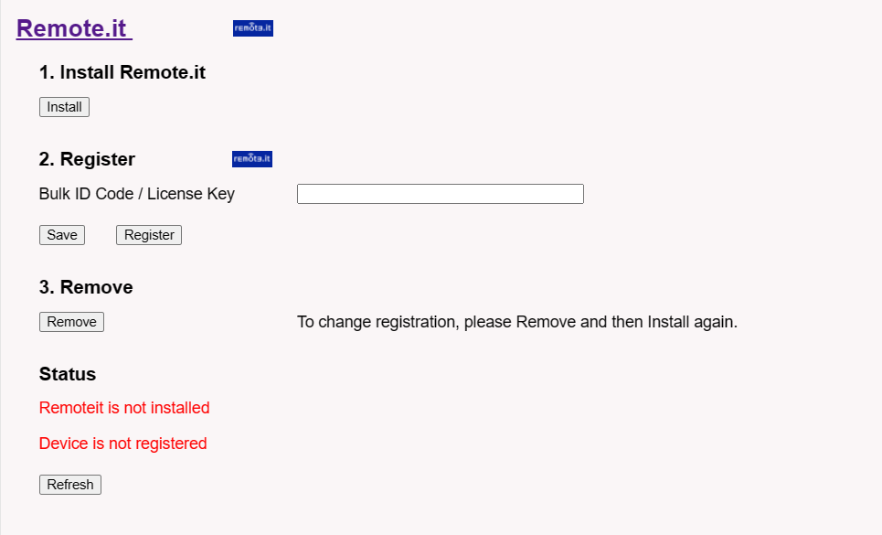
5.6.4 System --> Remote.it
In the System-> Remoteit interface, users can configure the gateway to be accessed remotely via Remote.it.
the users can refer to this link to configure them: Monitor & Remote Access Gateway
5.6.5 System --> Remote Mgnt & Auto Provision
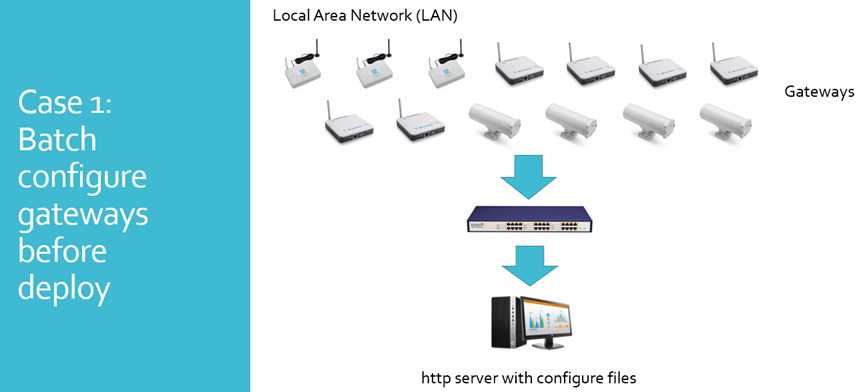
Auto Provision is the feature for batch configure and remote management. It can be used in below two cases:
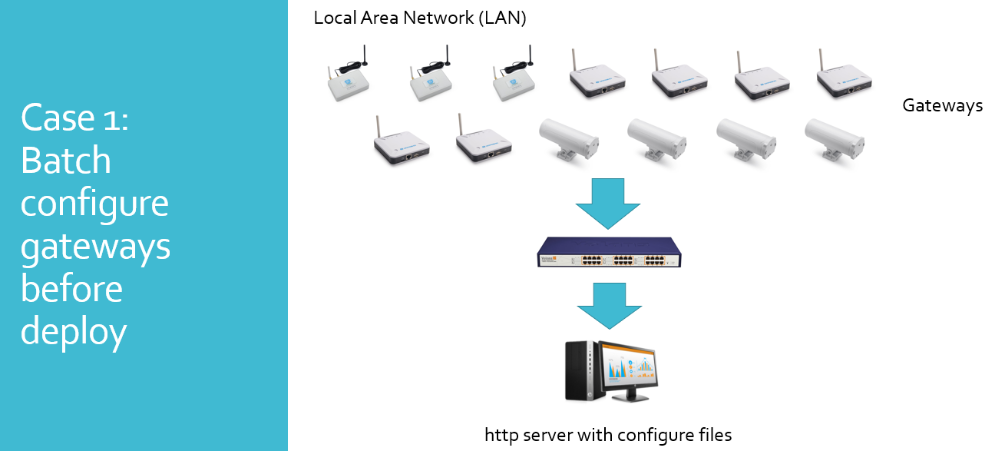
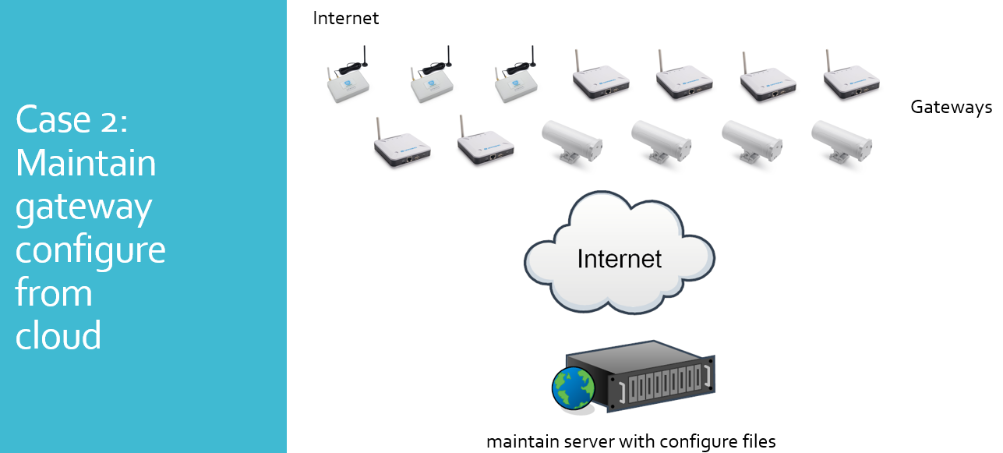
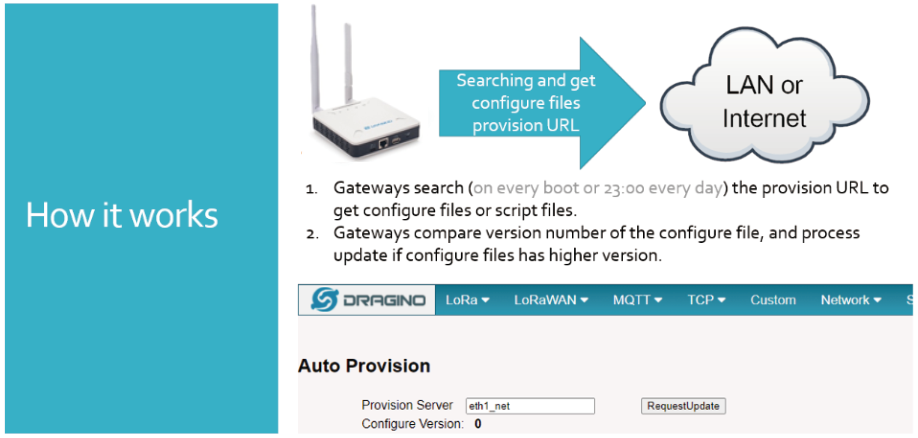
Please see this document for detail: http://www.dragino.com/downloads/index.php?dir=LoRa_Gateway/LPS8N/Firmware/Application_Note/&file=Auto-update-feature.pdf
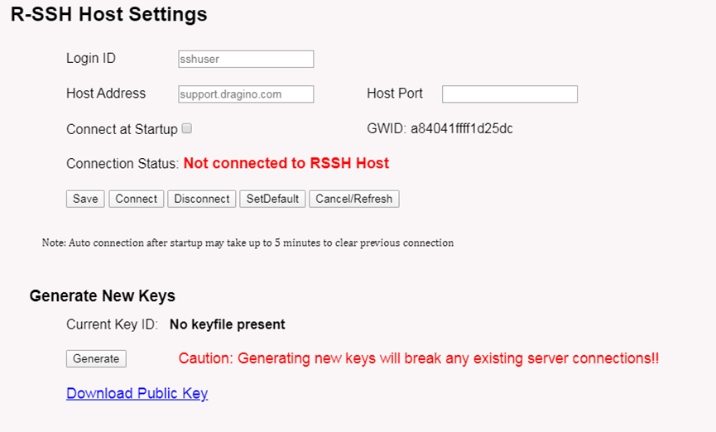
R-SSH is for remote access device and management, introduction for how to use: Remote Access Gateway
5.6.6 System --> Firmware Upgrade
We keep improving the LPS8N Linux side firmware for new features and bug fixes. Below are the links for reference.
- Latest firmware: LoRa Gateway Firmware,
( http://www.dragino.com/downloads/index.php?dir=LoRa_Gateway/LPS8N/Firmware)
- Change Log: Firmware Change Log.
( http://www.dragino.com/downloads/downloads/LoRa_Gateway/LPS8N/Firmware/ChangeLog )
The file named as xxxxx–xxxxx-squashfs-sysupgrade.bin is the upgrade Image. There are different methods to upgrade, as below.
Web--> System--> Firmware Upgrade

Select the required image and click Flash Image. The image will be uploaded to the device, and then click Process Update to upgrade.
NOTE: You normally need to uncheck the Preserve Settings checkbox when doing an upgrade to ensure that there is no conflict between the old settings and the new firmware. The new firmware will start up with its default settings.
The system will automatically boot into the new firmware after upgrade.
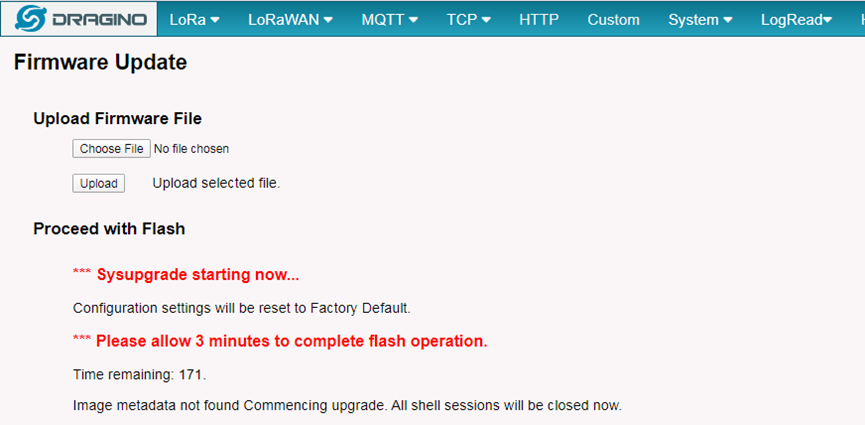
NOTE*: User can also upgrade firmware via Linux console
SCP the firmware to the system/var directory and then run
root@OpenWrt:~# /sbin/sysupgrade –n /var/Your_Image
NOTE : it is important to transfer the image in the /var directory, otherwise it may exceed the available flash size.
5.6.7 System --> Reboot/Reset

5.6.8 System --> Package Maintain

Place to show what package has installed and possible to upgrade packages.
5.7 LogRead
5.7.1 LogRead --> LoRa Log
Show the frequency for LoRa Radio and traffics.

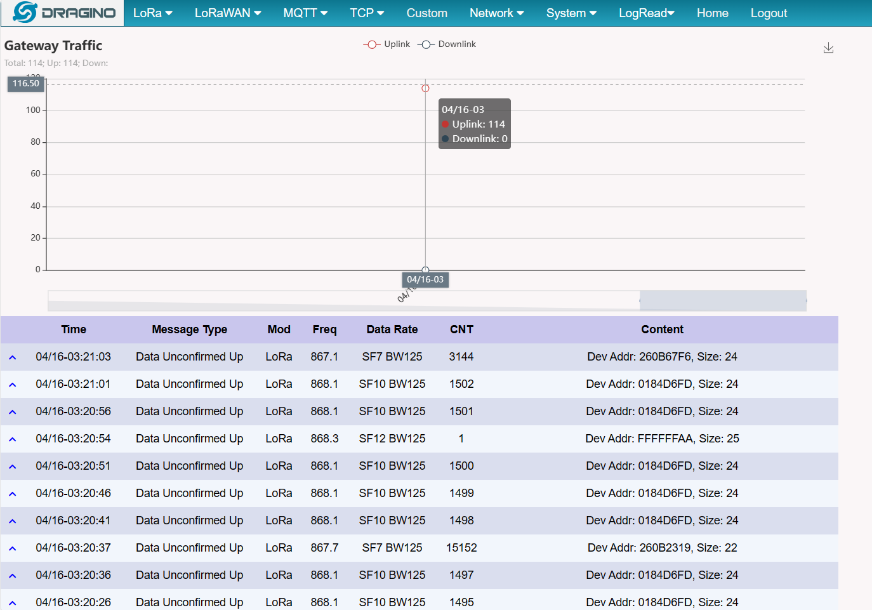
5.7.2 LogRead --> Gateway Traffic
Show the gateway traffic:
5.7.3 LogRead --> System Log
Show the system log
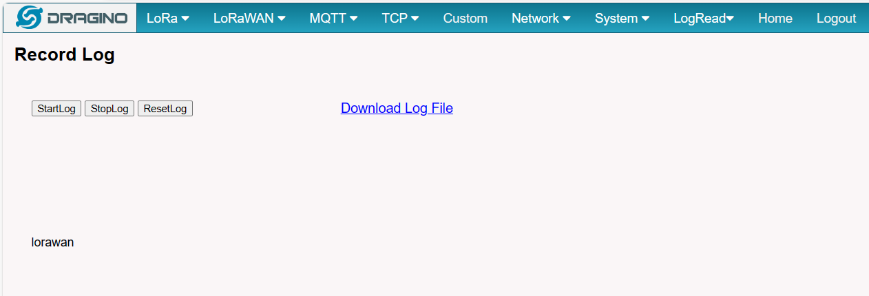
5.7.4 LogRead --> Record Log
This interface can record gateway logs:
For issue debug. User can Start Log --> Wait for 10 minutes --> Stop Log . Make sure this period include where issue happen. And then send the log to Dragino to debug.
6. More features
6.1 NTP Service/Time Synchronization
The gateway time sync service is provided by ntpd
1). Modify the NTP server address:
###Linux command
uci set system.ntp.server='0.openwrt.pool.ntp.org' #Required
uci add_list system.ntp.server='1.openwrt.pool.ntp.org' #Optional
uci add_list system.ntp.server='2.openwrt.pool.ntp.org' #Optional
uci add_list system.ntp.server='3.openwrt.pool.ntp.org' #Optional
uci commit system #Required
Note: If the NTP server is a Windows host, it may cause the time synchronization to fail,
6.2 Packet Filtering
Drop unwanted packets.
6.3 Remote Access
Remote Access Devices for management.
Instruction: http://wiki.dragino.com/xwiki/bin/view/Main/Monitor%20%26%20Remote%20Access%20Gateway/?Remote%20Access
6.4 How to decode ABP LoRaWAN node
Decode ABP:
6.5 How to set data to MQTT broker
Only support ABP LoRaWAN End Node
Instruction: http://wiki.dragino.com/xwiki/bin/view/Main/MQTT%20Forward%20Instruction/
6.6 How the gateway connects to Chirpstack v3/v4 via gateway-bridge
If the Chirpstack v3 Gateway-bridge is used, the corresponding gateway firmware must be used :
Chirpstack-gateway-bridge/Chirpstack-Bridge-V3.14.6-Bridge--build-v5.4.1679487778-20230322-2024/
Chirpstack v3 via gateway-bridge Instruction: http://wiki.dragino.com/xwiki/bin/view/Main/Notes%20for%20ChirpStack/#H4.A0A0HowthegatewayconnectstoChirpstackv3viagateway-bridge
If the Chirpstack v4 Gateway-bridge is used, the corresponding gateway firmware must be used :
Chirpstack-gateway-bridge/Chirpstack-Bridge-V4--build-v5.4.1670655072-20221210-1452/
Chirpstack v4 via gateway-bridge Instruction: http://wiki.dragino.com/xwiki/bin/view/Main/Notes%20for%20ChirpStack/#H4.A0HowthegatewayconnectstoChirpstackv4viagateway-bridge
Note: Different chirpstack versions use different gateway-bridge configurations.
After updating the Chirpstack gateway-bridge firmware, there is no need to re-download and install the Chirpstack gateway-bridge package
6.7 How does the gateway connect to Chirpstack via MQTT Forwarder
ChirpStack MQTT Forwarder is a MQTT packet forwarder for LoRa gateways. By default it forwards packets in Protobuf binary format, optionally it can be configured to use JSON encoding for debugging. In contrast to the ChirpStack Gateway Bridge, this component must always be installed on the gateway.
6.7.1 Configure Packet Forwarder
In the Dragino web-interface, you must configure the Packet Forwarder such that it forwards to localhost on port 1700.
By default, the web-interface can be accessed by entering the following URL in your browser: https://GATEWAY-IP-ADDRESS:8000 (replace GATEWAY-IP-ADDRESS by the actual IP address of your gateway). The default credentials are root / dragino.
- In the LoRaWAN menu, click LoRaWAN -- Semtech UDP
- Configure the following settings:
- Service Provider: Custom / Private LoRaWAN
- Server Address: localhost
- Uplink Port: 1700
- Downlink Port: 1700
- Click Save&Apply

6.7.2 Install ChirpStack MQTT Forwarder
SSH login
First user must login into the gateway using SSH,user can refer to the link to access the Linux console via SSH to the gateway: SSH Access for Linux console
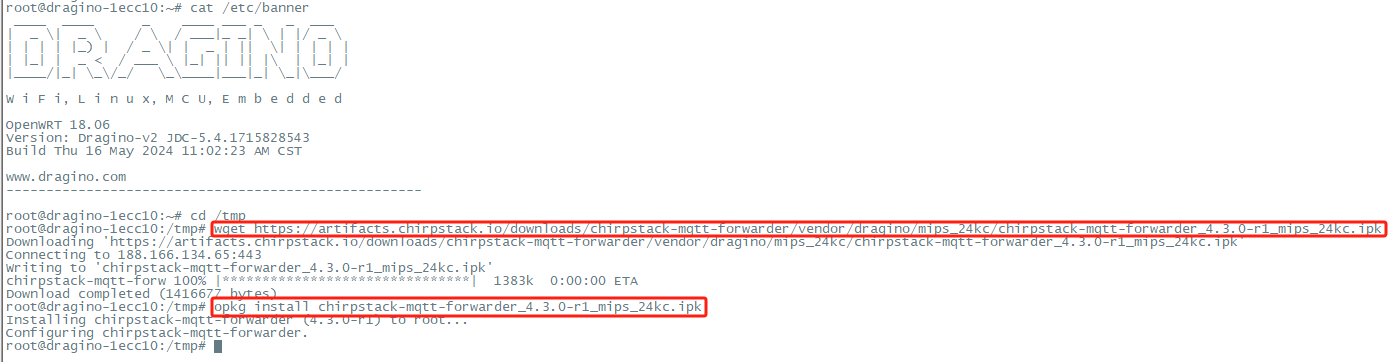
Download IPK
Use the following commands to download the latest version of the chirpstack-mqtt-forwarder package:
Install IPK
Use the opkg package-manager to install the downloaded package. Example:
Configuration
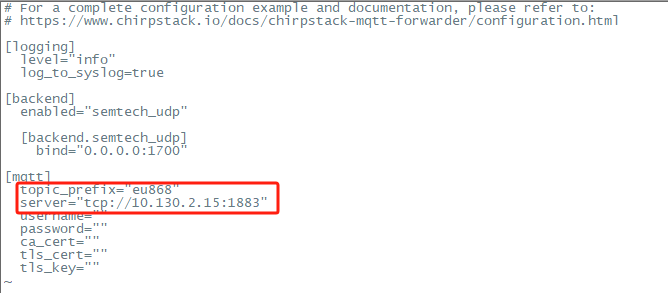
To connect the ChirpStack MQTT Forwarder to your MQTT broker, you must update the ChirpStack MQTT Forwarder configuration file.
This file is located at: /etc/chirpstack-mqtt-forwarder/chirpstack-mqtt-forwarder.toml
ChirpStack MQTT Forwarder Setting:
topic_prefix --> This corresponds to the frequency of the ChirpStack server
server --> Fill in the ChirpStack server address, Example: tcp://10.130.2.15:1883
username,password,ca_cert,tls_cert,tls_key parameters should be set as required.
Use commands to modify configuration files:
(Re)start and stop commands
Use the following commands to (re)start and stop the ChirpStack MQTT Forwarder service:
Check result
Use " logread -f " to check the operation of ChirpStack MQTT Forwarder.
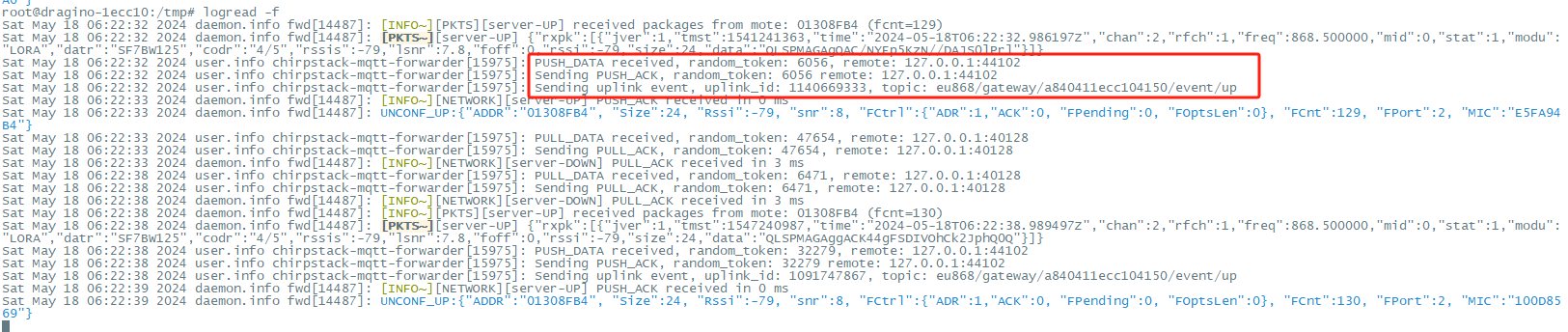
Go back to the Chirpstack server to check whether the gateway is "online" and whether the packets are displayed normally.

6.8 How to extend the gateway size of memory with USB device (SD/TF card, USB flash drive).
USB card reader plugged into the USB port of the gateway
Access the gateway Linux Command Line
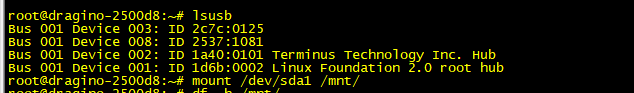
Check the USB device
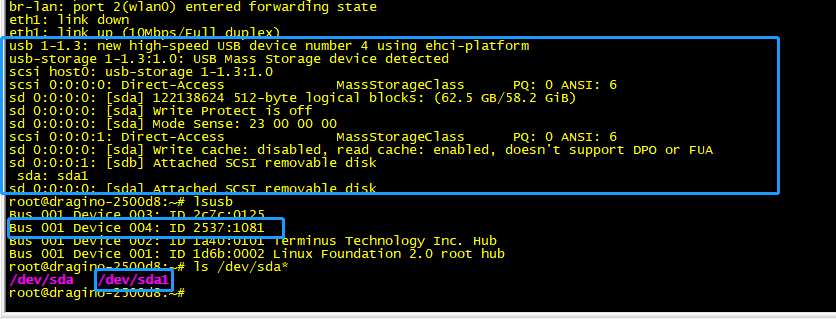
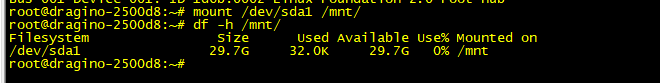
Mount the USB device
Set up the automatic mount on boot
6.9 More instructions
LoRaWAN Gateway Instruction(LoRaWAN Gateway)
6.10 Auto-Provision
Auto Provision is the feature for batch configure and remote management. It can be used in below two cases:
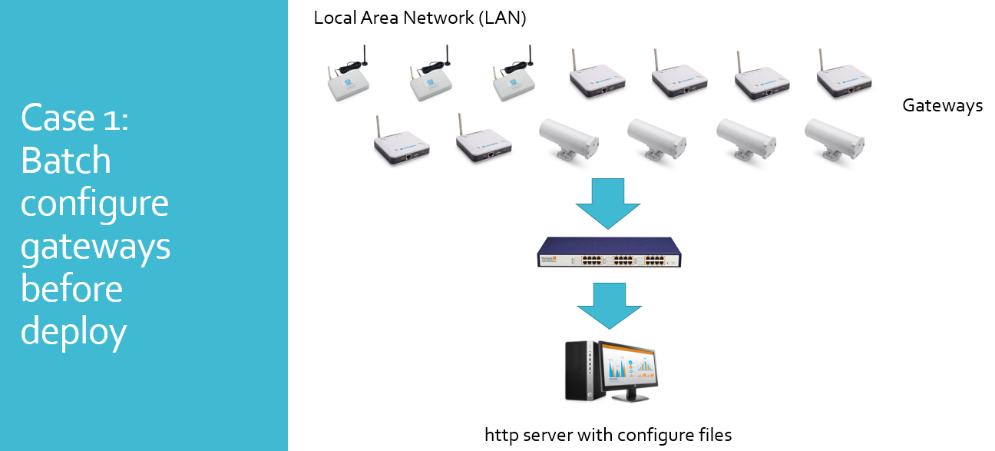
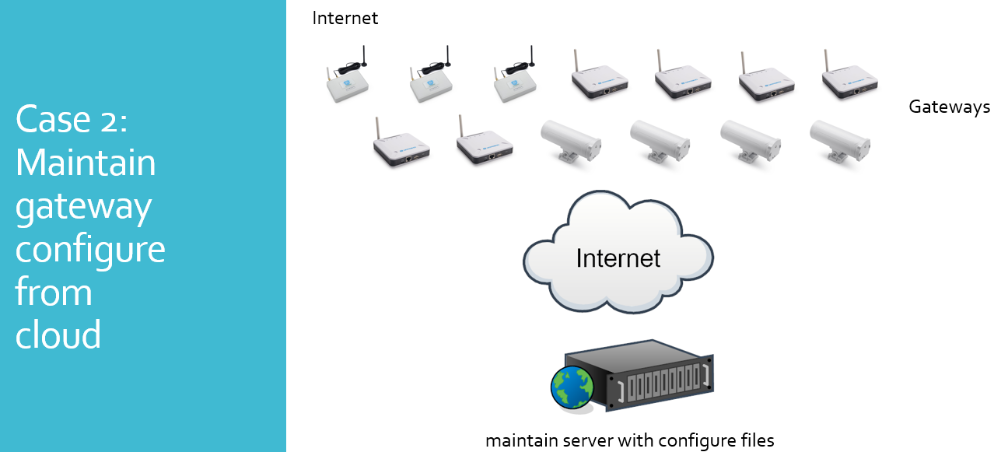
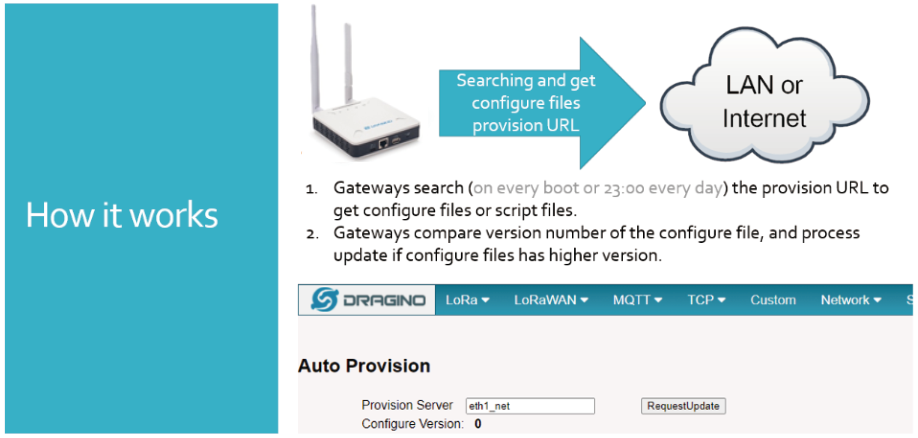
Please see this document for detail: http://www.dragino.com/downloads/index.php?dir=LoRa_Gateway/LPS8N/Firmware/Application_Note/&file=Auto-update-feature.pdf
7. Linux System
The LPS8N is based on the OpenWrt Linux system. It is open source, and users are free to configure and modify the Linux settings.
7.1 SSH Access for Linux console
User can access the Linux console via the SSH protocol. Make sure your PC and the LPS8N are connected to the same network, then use a SSH tool (such as putty in Windows) to access it.
IP address: IP address of LPS8N
Port: 22 (via WiFi AP mode) or 2222 (via WAN Interface)
User Name: root
Password: dragino (default)
After logging in, you will be in the Linux console and can enter commands as shown below.
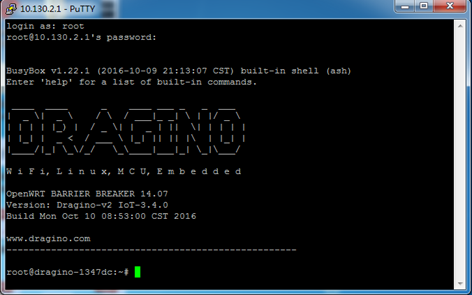
The “ logread -f” command can be used to debug how system runs.
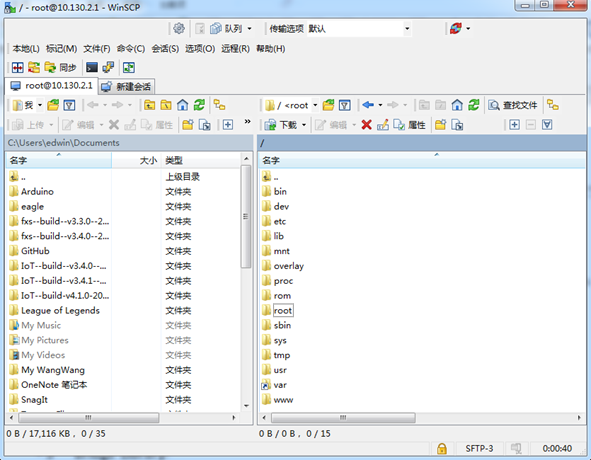
7.2 Edit and Transfer files
The LPS8N supports the SCP protocol and has a built-in SFTP server. There are many ways to edit and transfer files using these protocols.
In Windows, one of the easiest methods is using the WinSCP utility.
After establishing access via WinSCP to the device, you can use an FTP style window to drag / drop files to the LPS8N, or edit the files directly in the windows.
Screenshot is as below:
7.3 File System
The LPS8N has a 16MB flash and a 64MB RAM. The /var and /tmp directories are in the RAM, so contents stored in /tmp and /var will be erased after rebooting the device. Other directories are in the flash and will remain after reboot.
The Linux system uses around 8MB ~10MB flash size which means there is not much room for user to store data in the LPS8N flash.
You can use an external USB flash memory device to extend the size of flash memory for storage.
7.4 Package maintenance system
LPS8N uses the OpenWrt OPKG package maintenance system. There are more than 3000+ packages available in our package server for users to install for their applications. For example, if you want to add the iperf tool, you can install the related packages and configure LPS8N to use iperf .
Below are some example opkg commands. For more information please refer to the OPKG package maintain system (https://oldwiki.archive.openwrt.org/doc/techref/opkg)
In Linux Console run:
root@dragino-169d30:~# opkg update // to get the latest packages list
root@dragino-169d30:~# opkg list //shows the available packages
root@dragino-169d30:~# opkg install iperf // install iperf
The system will automatically install the required packages as shown below.
root@dragino-169d30:/etc/opkg# opkg install iperf
Installing iperf (2.0.12-1) to root…
Downloading http://downloads.openwrt.org/snapshots/packages/mips_24kc/base/iperf_2.0.12-1_mips_24kc.ipk
Installing uclibcxx (0.2.4-3) to root…
Downloading http://downloads.openwrt.org/snapshots/packages/mips_24kc/base/uclibcxx_0.2.4-3_mips_24kc.ipk
Configuring uclibcxx.
Configuring iperf.
8. Upgrade Linux Firmware
We keep improving the LPS8N Linux side firmware for new features and bug fixes. Below are the links for reference.
- Latest firmware: LoRa Gateway Firmware,
( http://www.dragino.com/downloads/index.php?dir=LoRa_Gateway/LPS8N/Firmware)
- Change Log: Firmware Change Log.
( http://www.dragino.com/downloads/downloads/LoRa_Gateway/LPS8N/Firmware/ChangeLog )
The file named as xxxxx–xxxxx-squashfs-sysupgrade.bin is the upgrade Image. There are different methods to upgrade, as below.
8.1 Upgrade via Web UI
Go to the page: Web --> System --> Firmware Upgrade
Select the required image and click Flash Image. The image will be uploaded to the device, and then click Process Update to upgrade.
NOTE: You normally need to uncheck the Preserve Settings checkbox when doing an upgrade to ensure that there is no conflict between the old settings and the new firmware. The new firmware will start up with its default settings.
The system will automatically boot into the new firmware after upgrade.
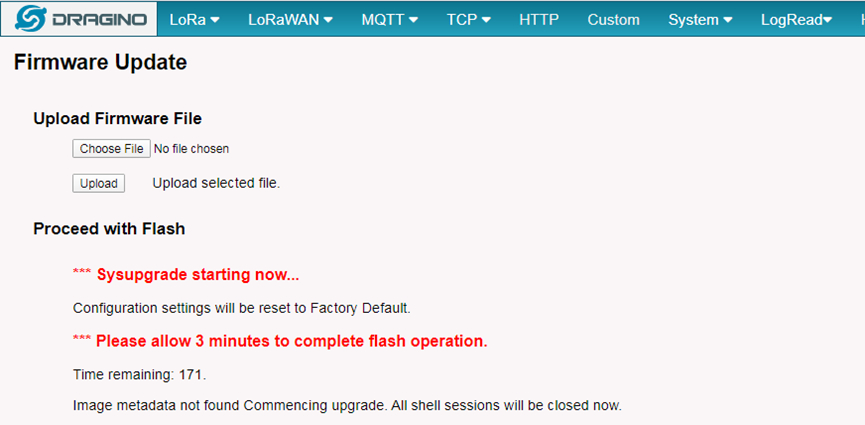
8.2 Upgrade via Linux console
SCP the firmware to the system /var directory and then run
root@OpenWrt:~# /sbin/sysupgrade –n /var/Your_Image
NOTE: it is important to transfer the image in the /var directory, otherwise it may exceed the available flash size.
9. OTA System Update
LPS8N supports system auto update via OTA, please see this URL for the detail of this feature.
10. FAQ
10.1 How can I configure for a customized frequency band?
See below link for how to customize frequency band: How to customized LoRaWAN frequency band
10.2 Can I make my own firmware for the gateway, where can I find the source code?
Yes, You can make your own firmware for the LPS8N for branding purposes or to add customized applications.
The source code and compile instructions can be found at: https://github.com/dragino/openwrt_lede-18.06
10.3 Can I use 868Mhz version for 915Mhz bands?
It is possible but the distance will be very short, you can select US915 frequency band in 868Mhz version hardware. It will work but you will see the performance is greatly decreased because the 868Mhz version has an RF filter for band 863~870Mhz, all other frequencies will have high attenuation.
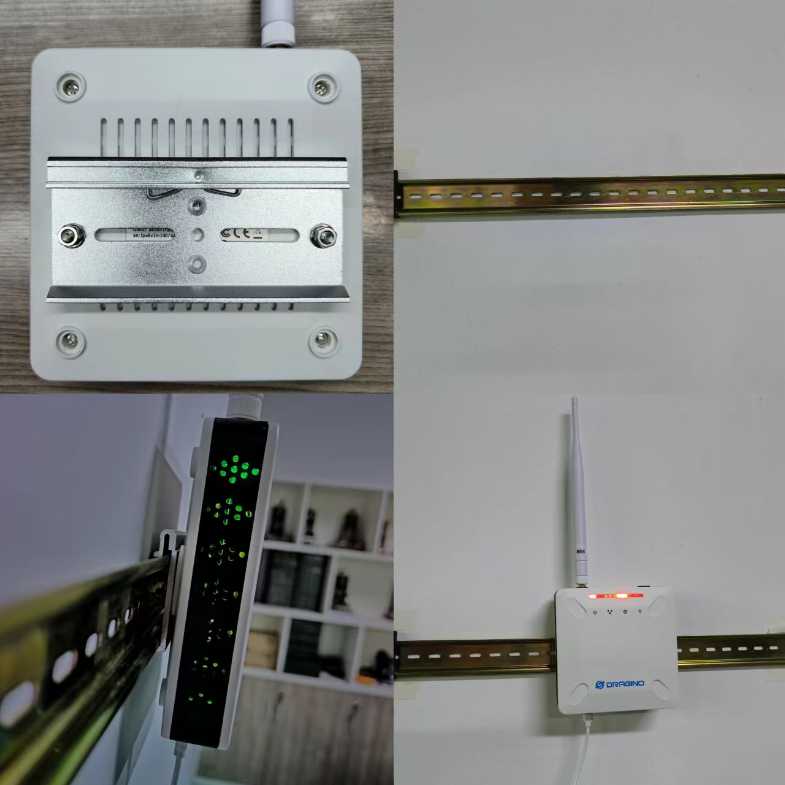
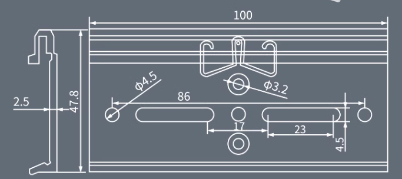
10.4 DIN Rail Mounting Reference.

11. Trouble Shooting
11.1 I get kernel error when install new package, how to fix?
In some cases, when installing a package with opkg, it will generate a kernel error such as below due to a mismatch I the kernel ID:
root@dragino-16c538:~# opkg install kmod-dragino2-si3217x_3.10.49+0.2-1_ar71xx.ipk
Installing kmod-dragino2-si3217x (3.10.49+0.2-1) to root…
Collected errors:
* satisfy_dependencies_for: Cannot satisfy the following dependencies for kmod-dragino2-si3217x:
* kernel (= 3.10.49-1-4917516478a753314254643facdf360a) *
* opkg_install_cmd: Cannot install package kmod-dragino2-si3217x.
In this case, you can use the –force-depends option to install such package as long as the actual kernel version is the same.
Opkg install kmod-dragino2-si3217x_3.10.49+0.2-1_ar71xx.ipk –force-depends
11.2 How to recover the LPS8N if the firmware crashes
Please follow this instruction to recover your gateway: Recover Gateway
11.3 I configured LPS8N for WiFi access and lost its IP. What to do now?
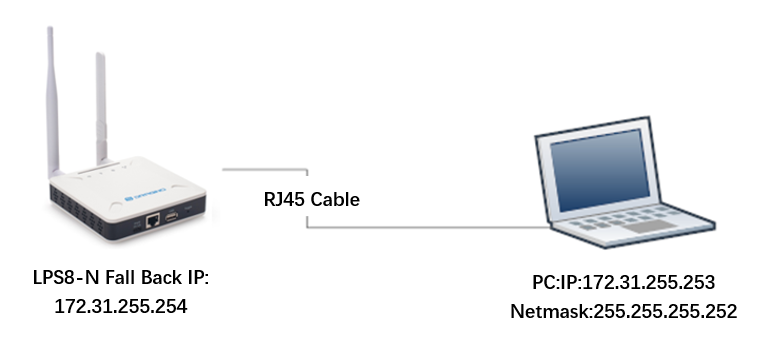
The LPS8N has a fall-back IP address on its WAN port. This IP is always enabled so you can use the fall-back IP to access LPS8N no matter what the WiFi IP is. The fall back IP is useful for connecting and debug the unit.
Note: fallback IP can be disabled in the WAN and DHCP page.
Steps to connect via fall back IP:
1. Connect PC's Ethernet port to LPS8N's WAN port
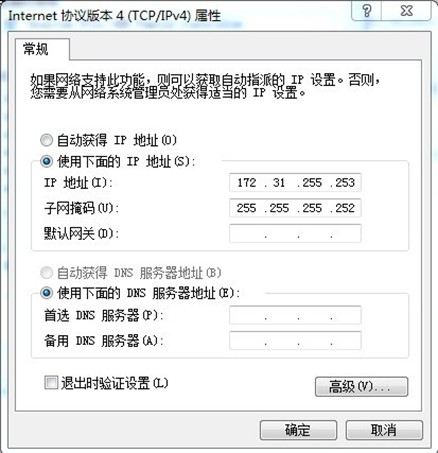
2. Configure PC's Ethernet port has
IP: 172.31.255.253 and
Netmask: 255.255.255.252
As below photo:
3. In the PC, use IP address 172.31.255.254 to access the LPS8N via Web or Console.
Please note the latest firmware uses port 8000 for http and 2222 for ssh access.
11.4 I connect to the LPS8N's SSID but LPS8N didn't assign DHCP IP to my laptop?
This is a known bug for the firmware version before 2019-09-23 for LPS, the issue was fixed since version: LG02_LG08--build-v5.2.1569218466-20190923-1402.
In the old version, user can use the fall back ip method to access and configure the device.
11.5 When i power on LPS8N , i can only see PWR LED is on. other LEDs are not blinking.
If there is no LED blink except the PWR led. There might be:
1) Power adapter issue. In this case, please try another power adapter.
2) Mother Board broken.
11.6 Why does the gateway reboot every 15 minutes without Internet?
Check whether Internet Detect is enabled on the System-->General interface.
Internet Detect is enabled by default. When there is no gateway network, it will reboot after 15 minutes.

12. Order Info
Part Number: LPS8N-XXX-YYY or LPS8NP-XXX-YYY
XXX: Frequency Band
- 868 : valid frequency: 863Mhz ~ 870Mhz. for bands EU868, RU864, IN865 or KZ865.
- 915: valid frequency: 902Mhz ~ 928Mhz. for bands US915, AU915, AS923 or KR920
YYY: 4G Cellular Option
- EC25-E: EMEA, Korea, Thailand, India.
- EC25-AFX: America:Verizon, AT&T(FirstNet), U.S.Cellular; Canada:Telus
- EC25-AUX: Latin America, New Zeland, Taiwan
- EC25-J: Japan, DOCOMO, SoftBank, KDDI
More info about valid bands, please see EC25-E product page.
13. Packing Info
Package Includes:
- LPS8N/ LPS8NP LoRaWAN Gateway x 1
- Stick Antenna for LoRa RF part. Frequency is one of 470 or 868 or 915Mhz depends the model ordered
- Packaging with environmental protection paper box
Dimension and weight:
- Device Size: 12 x 12 x 3 cm
- Weight: 187g
- Package Size: 14.5 x 13.5 x 6 cm
- Weight: 300g
14. Support
- Try to see if your questions already answered in the wiki.
- Support is provided Monday to Friday, from 09:00 to 18:00 GMT+8.
Due to different timezones we cannot offer live support. However, your questions will be answered as soon as possible in the before mentioned schedule. - Provide as much information as possible regarding your enquiry (product models, accurately describe your problem and steps to replicate it etc) and send a mail to:support@dragino.com