Notes for TTN
Table of Contents:
- 1. The Things Network-V3
- 2. Gateway Registration for Semtech UDP
- 3. Gateway Registration for Basics Station
- 4. Configure node connection to TTNv3
- 5. TTN V3 integrated into MQTT server
- 6. Route TTN data to Node-Red
- 7. Request Remote Support
1. The Things Network-V3
1.1 Introduction
1.1.1 What is The Things Network
The Things Network is a global collaborative Internet of Things ecosystem that creates networks, devices and solutions using LoRaWAN.
The Things Network runs The Things Stack Community Edition, which is a crowdsourced, open and decentralized LoRaWAN network. This network is a great way to get started testing devices, applications, and integrations, and get familiar with LoRaWAN.
1.1.2 Login or crate an account
Login or create an account to get started with The Things Network and start using The Things Stack Console.
Once you have an account,get started by following steps for adding Gateway,Device and Intergrations.
1.1.3 List the support products and Requirements
LoRaWAN Gateway model: Existing Gateway
2. Gateway Registration for Semtech UDP
2.1 Primary LoRaWAN Server
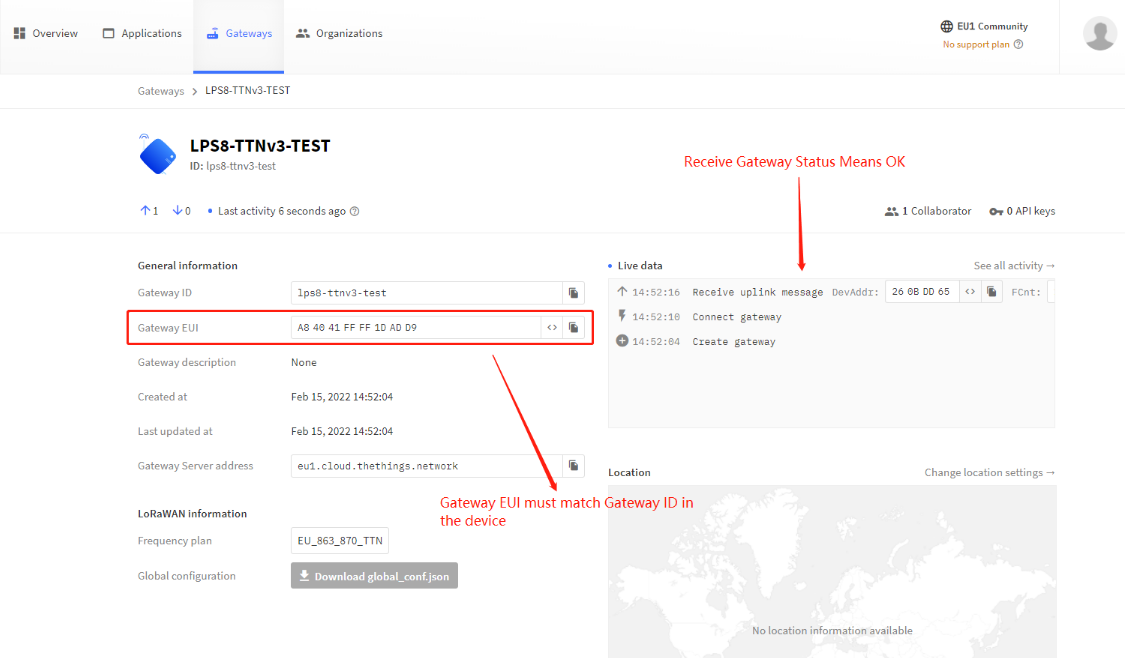
Register Gateway
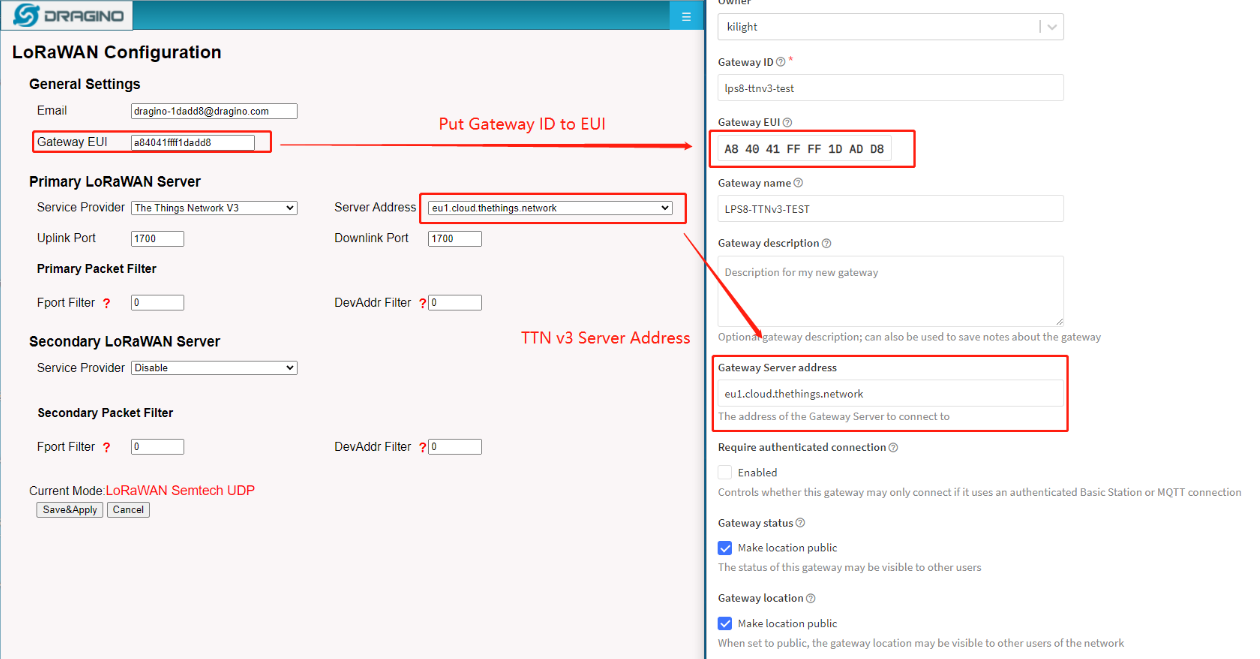
Put Gateway ID
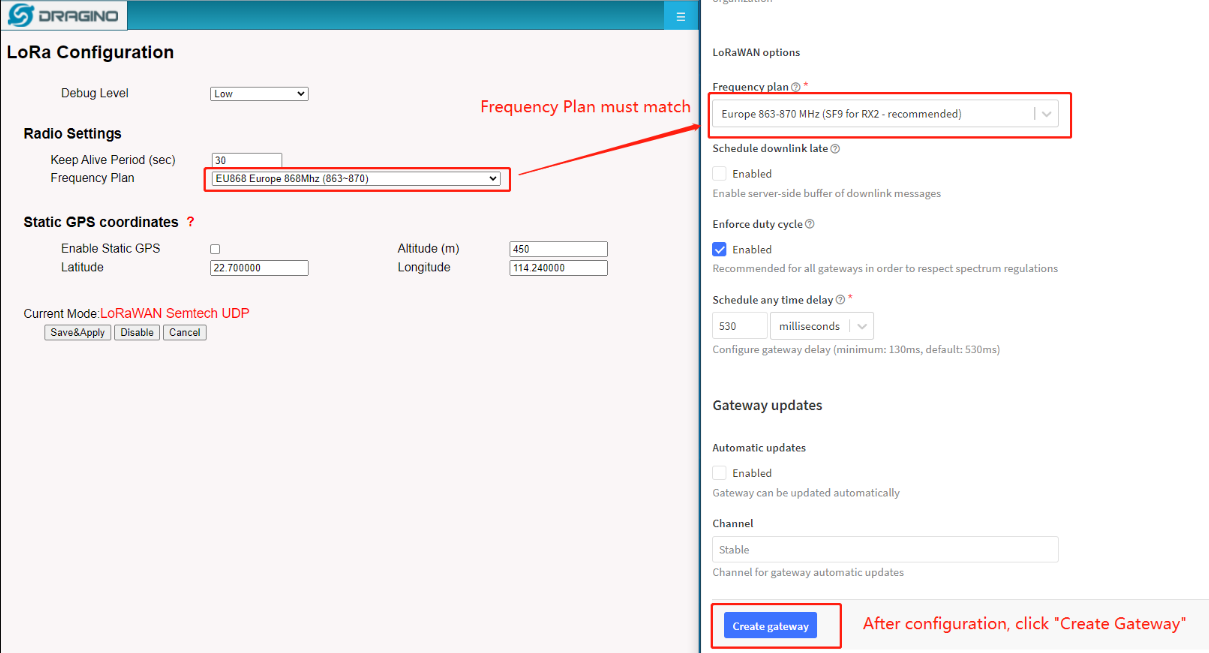
Choose Frequency Band
Note:
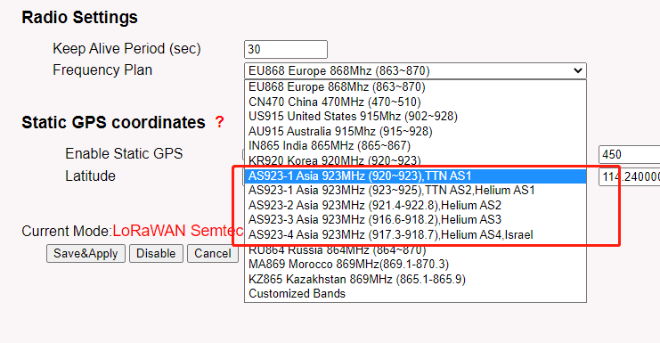
DRAGINO - Frequency Plan list --------------- The Thing Network Frequency Plan List
AS923-1 (920-923) --------------- Asia 920-923 Mhz
AS923-1 (923-925) --------------- Asia 915-928 Mhz (AS923 Group 1)with only default channels
AS923-2 (921.4-922.8) --------------- Asia 920-923 Mhz (AS923 Group 2)with only default channels
AS923-3 (916.6-918.2) --------------- Asia 915-921 Mhz (AS923 Group 3)with only default channels
AS923-4 (917.3-918.7) --------------- Asia 917-920 Mhz (AS923 Group 4)with only default channels
Show Status
2.2 Secondary LoRaWAN Server
2.2.1 Introduction
The Dragino gateway has supports the Secondary server settings.
2.2.2 Below list the support products and Requirements:
2. Firmware version since : lgw--build-v5.4.1644658774
2.2.3 Example
The following takes Helium as a Secondary LoRaWAN server as an example
2.2.4 Step 1: Download and Install the helium gateway-rs
The users is needing to download and install the helium gateway-rs then click the button of Save&Apply.
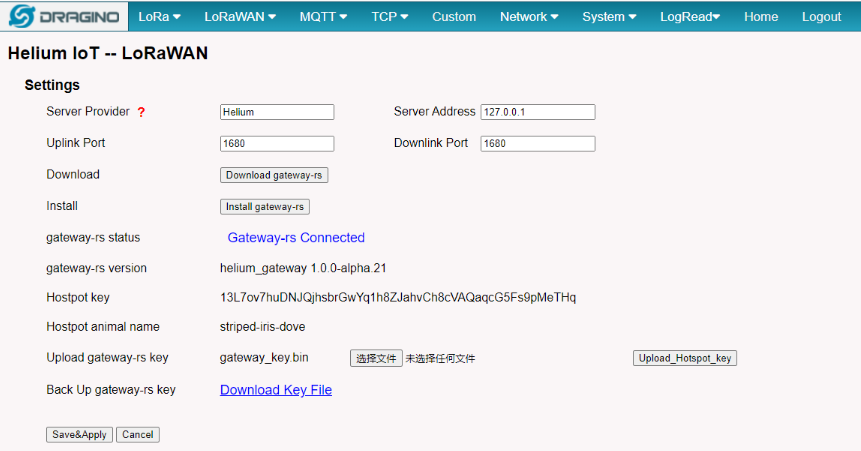
Download and Install gateway-rs
2.2.5 Step 2: Back to Semtech UDP page
Back to the page of Semtech UDP check the secondary server settings and click the button of Save&Apply.
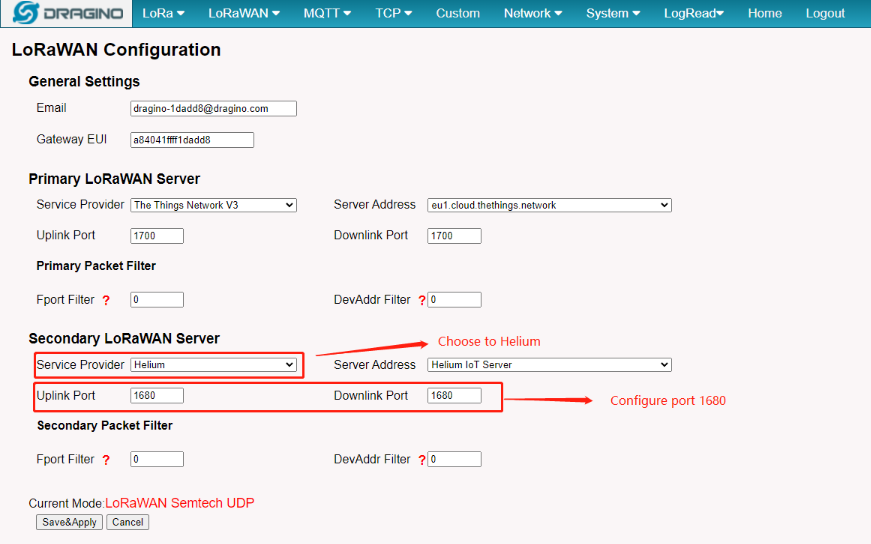
Configuration of helium
3. Gateway Registration for Basics Station
3.1 Introduction
The LoRa Basics™ Station protocol simplifies management of large scale LoRaWAN networks. LoRa Basics™ Station is the preferred way of connecting Gateways to The Things Stack. The LoRa Basics Station doc
Below list the support products and Requirements:
2. Firmware version since : lgw--build-v5.4.1640315898
What do you need to prepare
A gateway that can access the internet normally
3.2 Step 1: Add Gateway
The example for EU:
User can add your gateway into The Things Network V3 according to the previous step
Following picture is the successful added.
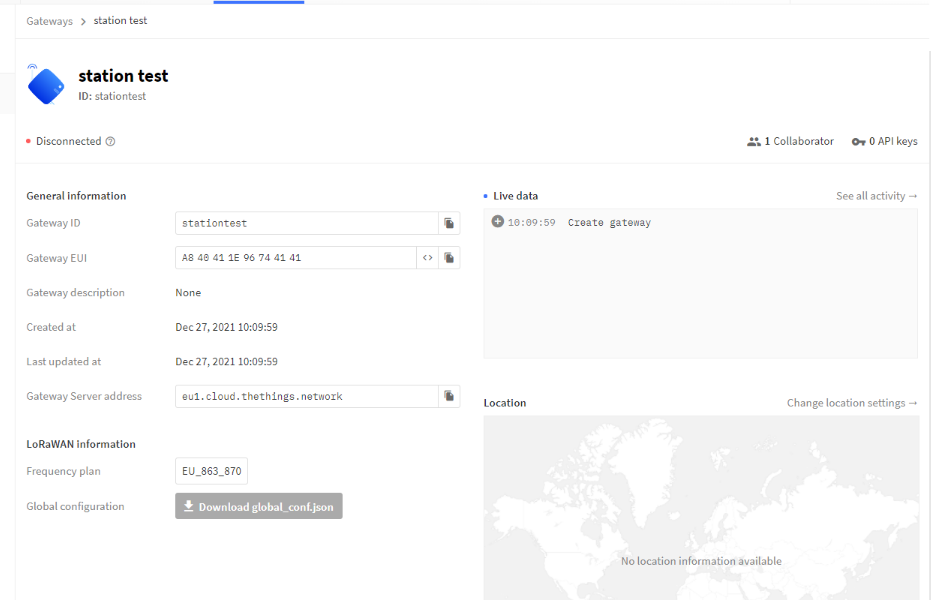
Add Gateway
3.3 Step 2: Create the API key
user need to create the CUPS API key and LNS API key.
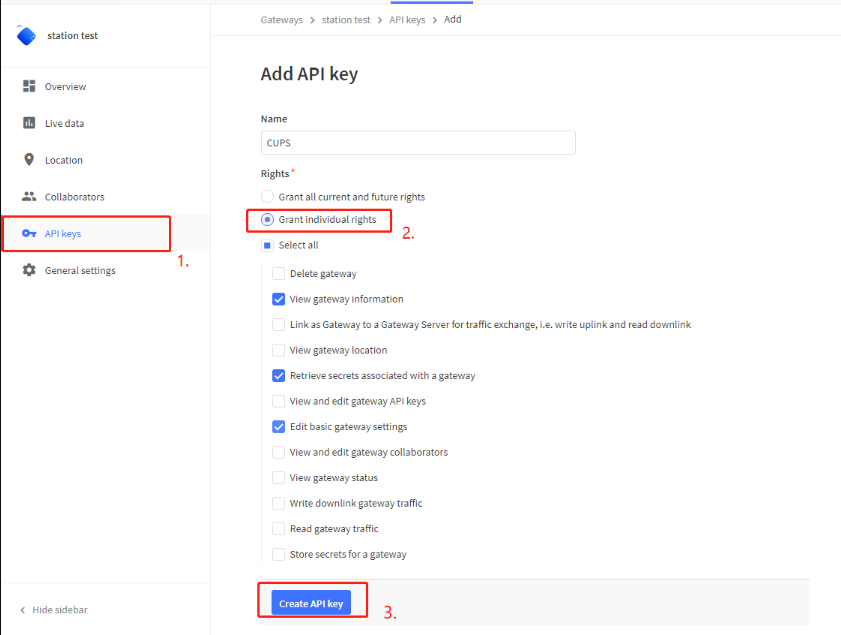
Create CUPS API key
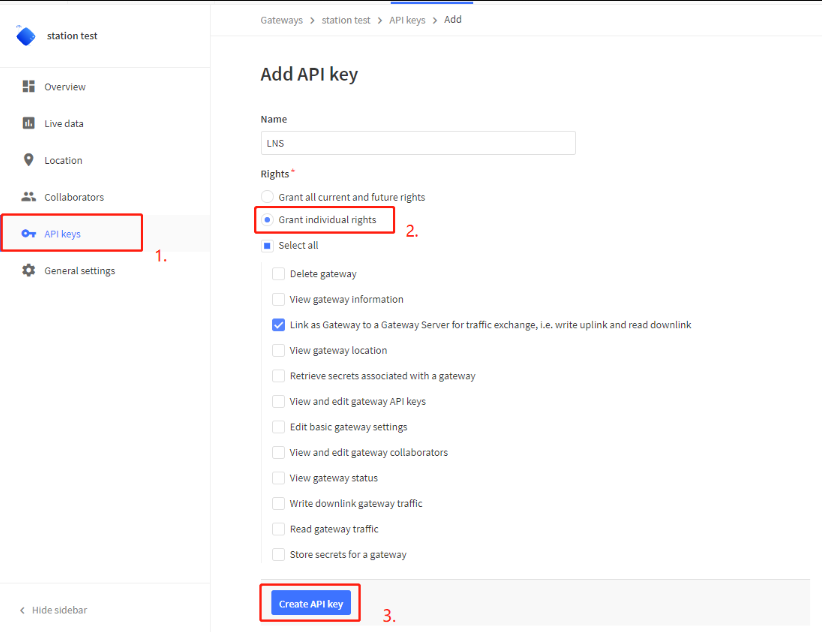
Create LNS API key
Note : Please copy the API key.
3.4 Step 3: Update the gateway setting
In the LoRa Basics Station LNS Authentication Key field, paste the API key you generated in the previous step.
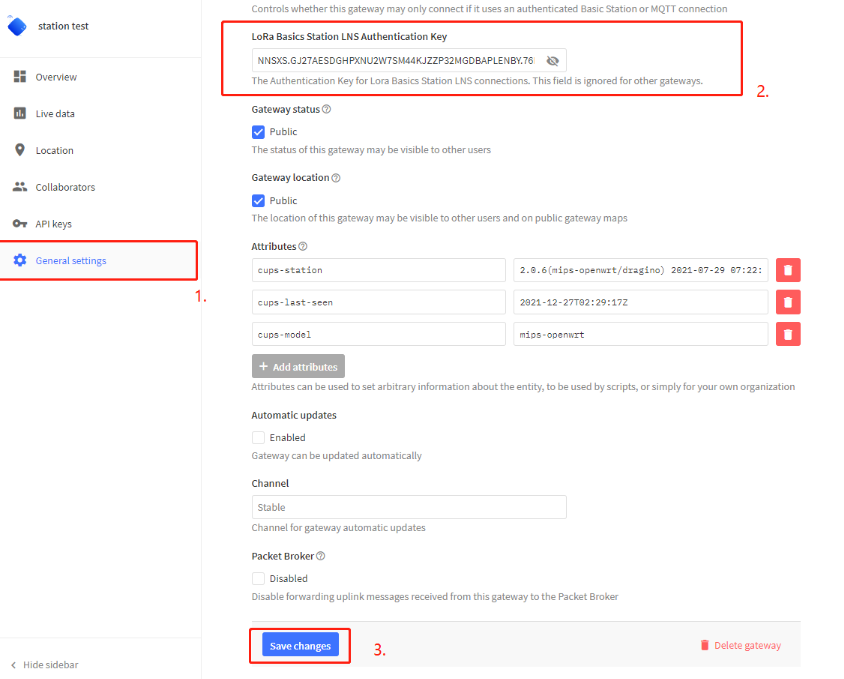
paste the API key
3.5 Step 4: Access the gateway GUI
User need to update the API key and install the Certificate
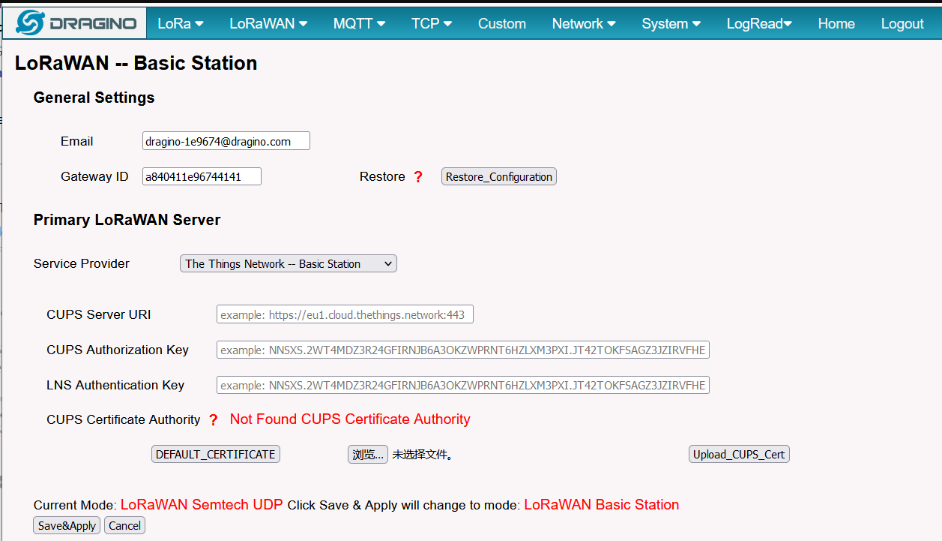
Access the gateway GUI
3.6 Step 5: Configure Station
User need to input Server URI, Server CUPS Key and LNS Key, as well as install CUPS certificate.
just to clarify:
CUPS Server URI --> Server Adress
CUPS Authorization Key --> Server CUPS API Key
LNS Authorization Key --> Server LNS API Key
CUPS certificate --> Server CA(user can use the button to install the certificate by default)
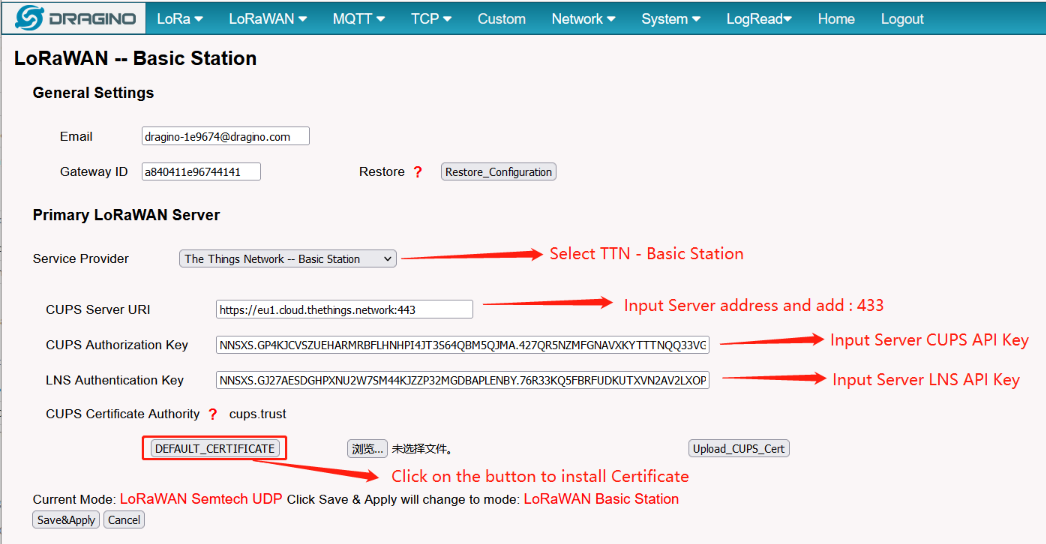
Congfigure Station
3.7 Start Station
When the user has finished the configuration,Please click Sace&Apply to start station to connect The Things Network.
3.8 Siccessful Connection
If user completes the above steps,which will see live date in the TTN.
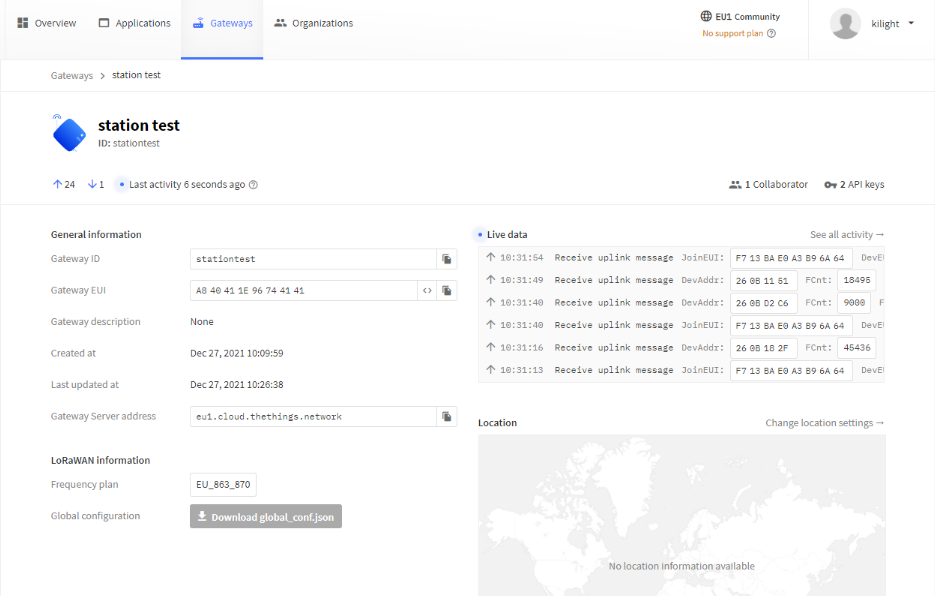
Station live date
3.9 Trouble Shooting
User can check the station log in the LogRead --> System Log page.
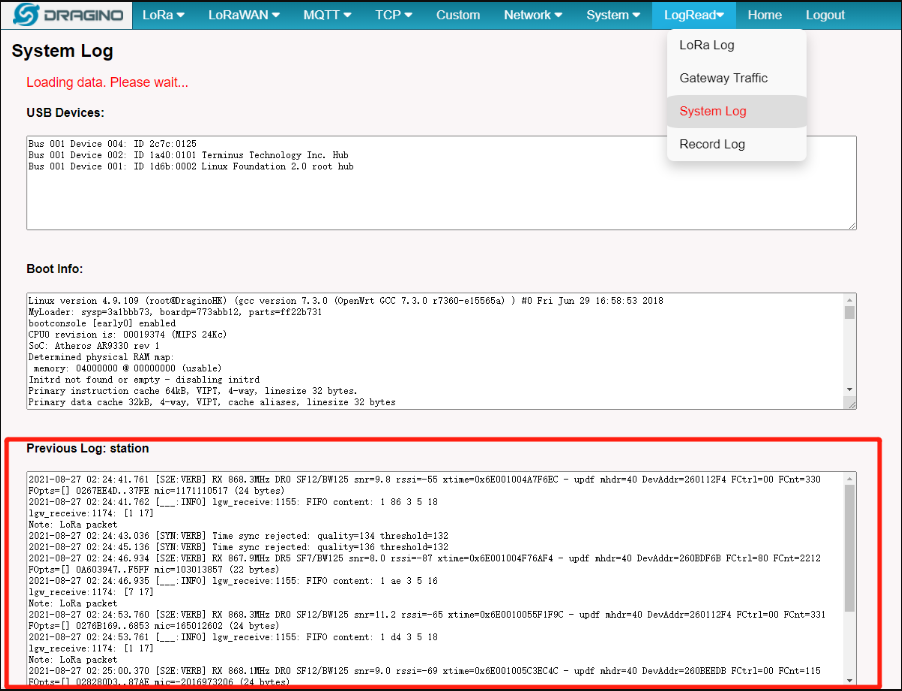
Station Log
and recode the station log in the LogRead --> Recode Log page.
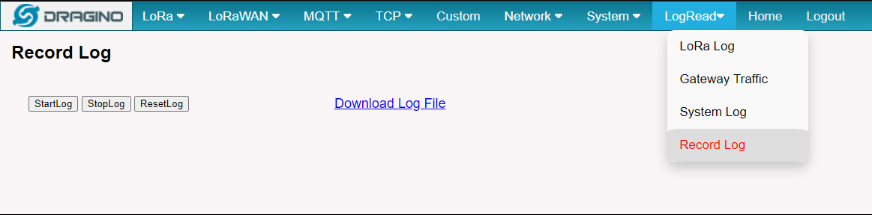
Recore Log
4. Configure node connection to TTNv3
Following is an example for how to join the TTN v3 LoRaWAN Network.
The gateway is already set up to connect to the TTN network, so we now need to configure the TTNv3 server.
We take LES01 as an example.
4.1 Step 1
Create a device in TTN with the OTAA keys from LSE01.
Each LSE01 is shipped with a sticker with the default device EUI as below:
You can enter this key in the LoRaWAN Server portal. Below is TTN screen shot:
4.2 Step 2
There are all our nodes in the repository. Users can choose the corresponding brand, model, firmware version and frequency.The decoder and configuration information of the node are pre-configured.Users do not need to configure them.
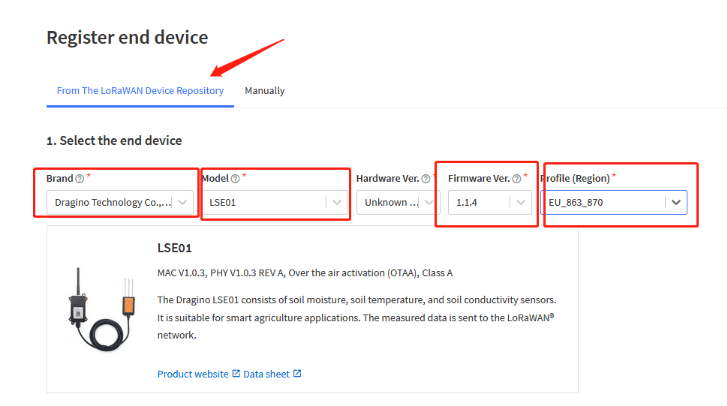
4.3 Step 3
Add APP EUI in the application:
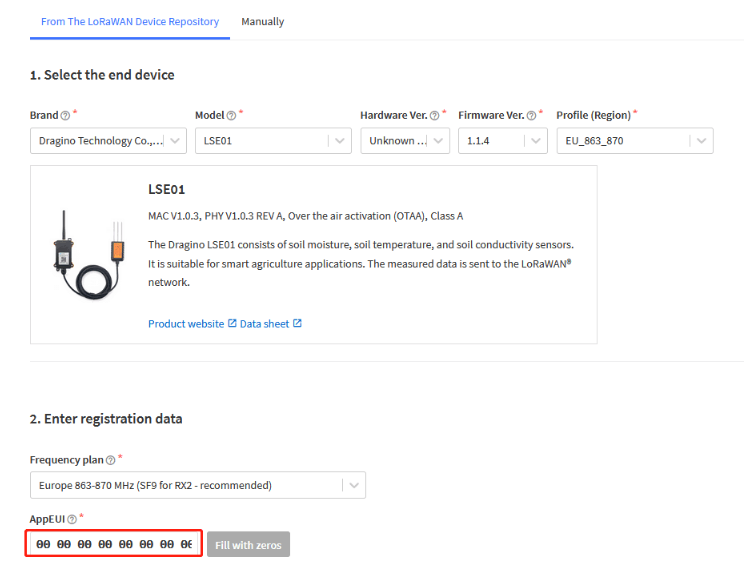
4.4 Step 4
Add APP KEY and DEV EUI:
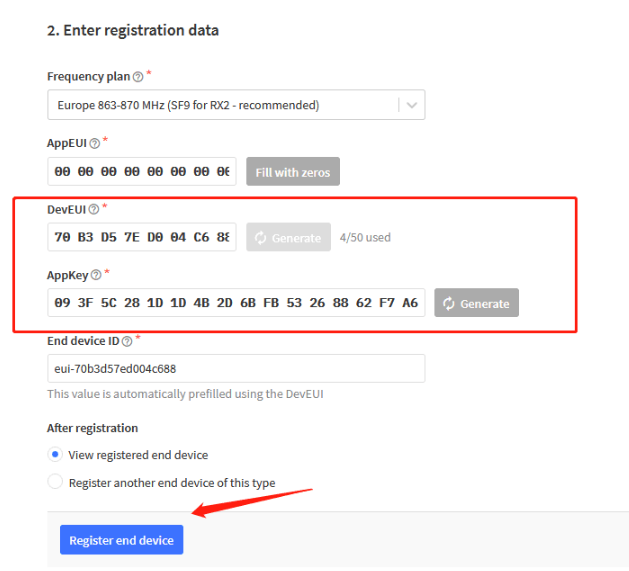
5. TTN V3 integrated into MQTT server
5.1 Introduction
The Application Server exposes an MQTT server to work with streaming events. In order to use the MQTT server you need to create a new API key, which will function as connection password. You can also use an existing API key, as long as it has the necessary rights granted.
5.2 Create device steps at MQTT
The user creates a new API KEY after creating a device on TTN V3.
Then copy the password and open MQTT.fx.
Fill in Broker Address and Broker port.
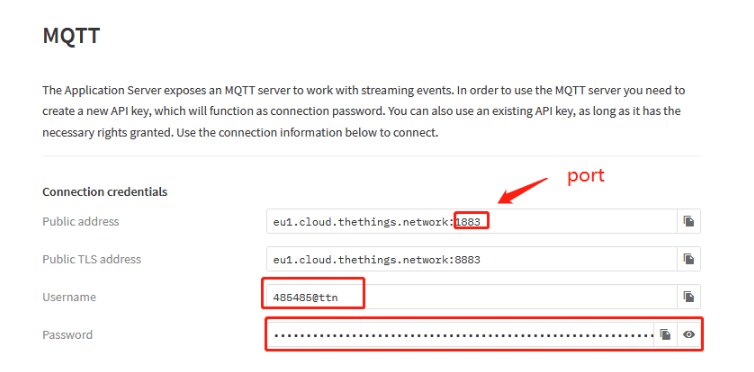
Fill in the username and password into MQTT.
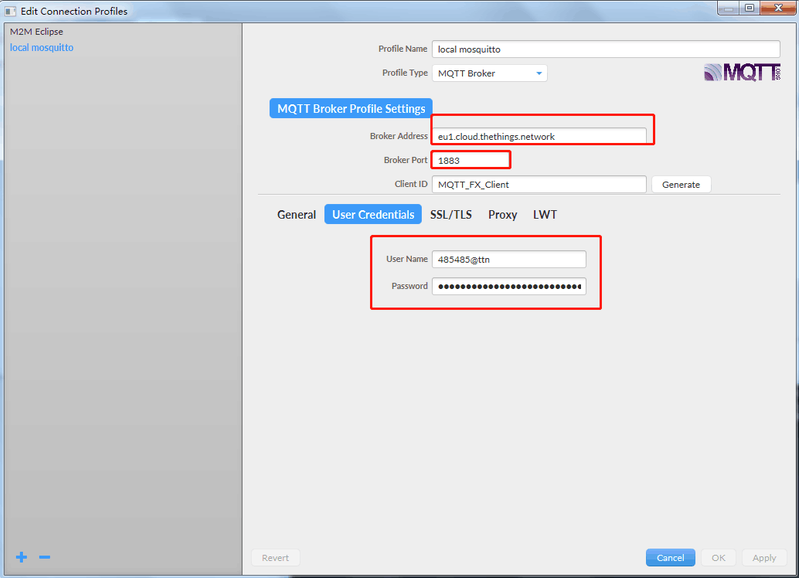
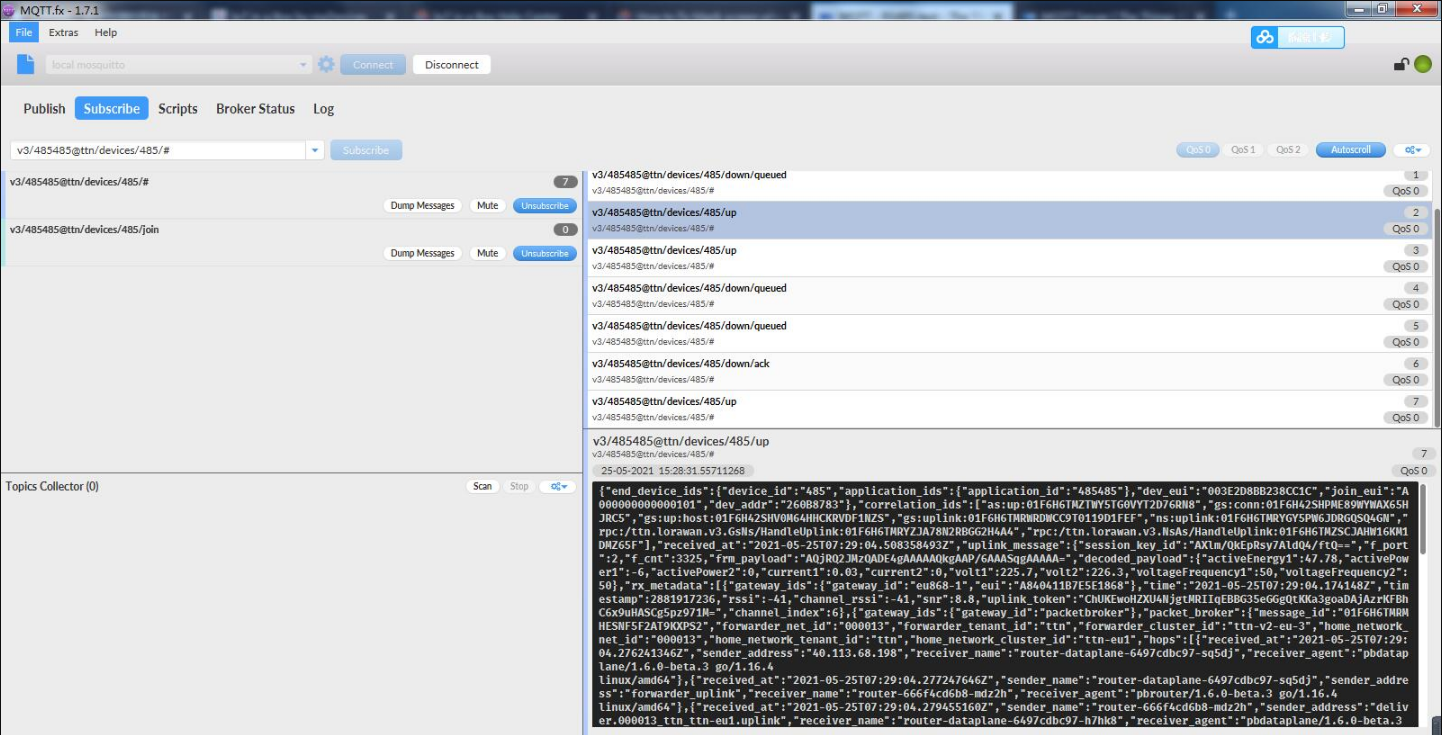
The Application Server publishes uplink traffic on the following topics:
v3/{application id}@{tenant id}/devices/{device id}/join
v3/{application id}@{tenant id}/devices/{device id}/up
v3/{application id}@{tenant id}/devices/{device id}/down/queued
v3/{application id}@{tenant id}/devices/{device id}/down/sent
v3/{application id}@{tenant id}/devices/{device id}/down/ack
v3/{application id}@{tenant id}/devices/{device id}/down/nack
v3/{application id}@{tenant id}/devices/{device id}/down/failed
v3/{application id}@{tenant id}/devices/{device id}/service/data
v3/{application id}@{tenant id}/devices/{device id}/location/solved
Note: Remember that the format of these topics for The Things Stack Open Source would contain {application id} instead of {application id}@{tenant id}.
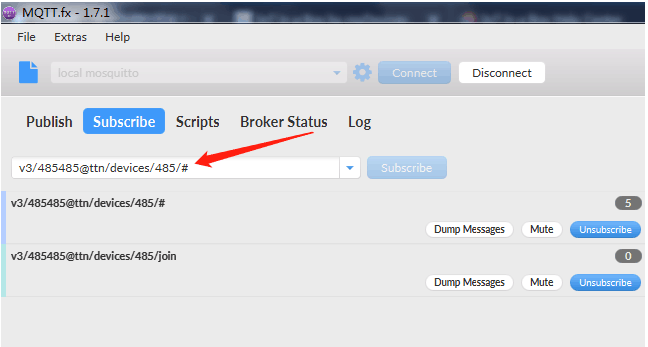
While you could subscribe to all of these topics separately, for the simplicity of this tutorial we use # to subscribe to all topics, i.e. to receive all uplink traffic.
Downlinks can be scheduled by publishing the message to the topic v3/{application id}@{tenant id}/devices/{device id}/down/push.
Note: Remember that the format of this topic for The Things Stack Open Source deployment would be v3/{application id}/devices/{device id}/down/push.
Instead of /push, you can also use /replace to replace the downlink queue. Replacing with an empty array clears the downlink queue. Example:
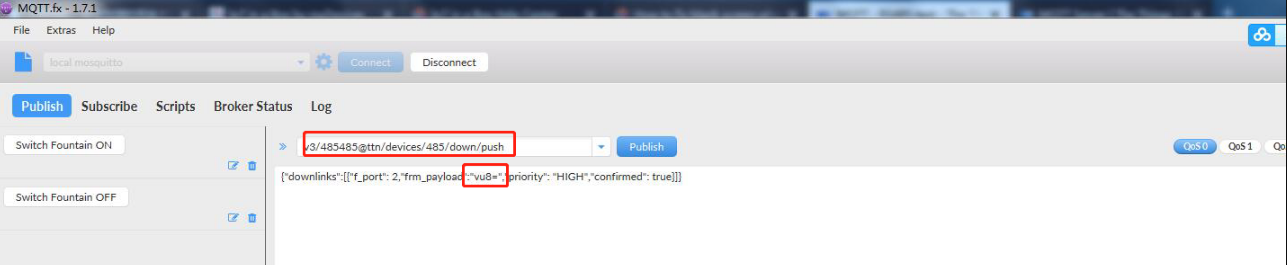
To send an unconfirmed downlink message to the device dev1 in application app1 in tenant tenant1 with the hexadecimal payload BE EF on FPort 15 with normal priority, use the topic v3/app1@tenant1/devices/dev1/down/push with the following contents:
Note: Use this handy tool to convert hexadecimal to base64.
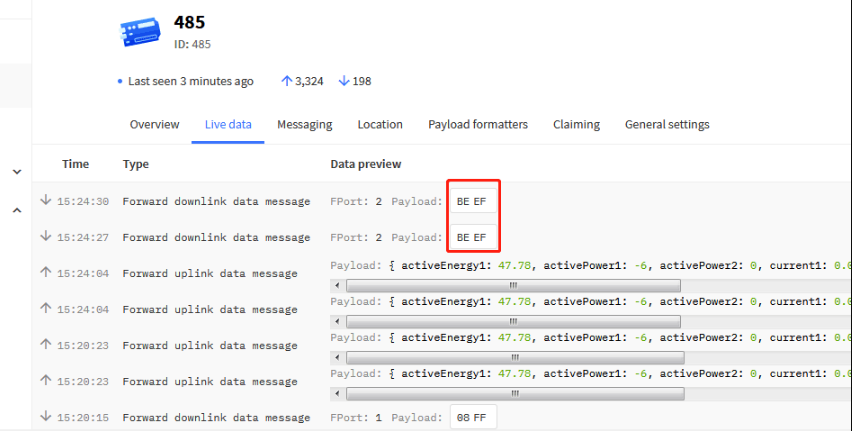
5.3 Send Downlink message
How to configure downlink in TTN V3?
A few examples: set the transmission interval to 90 seconds.
Downlink command: 01 00 00 5A
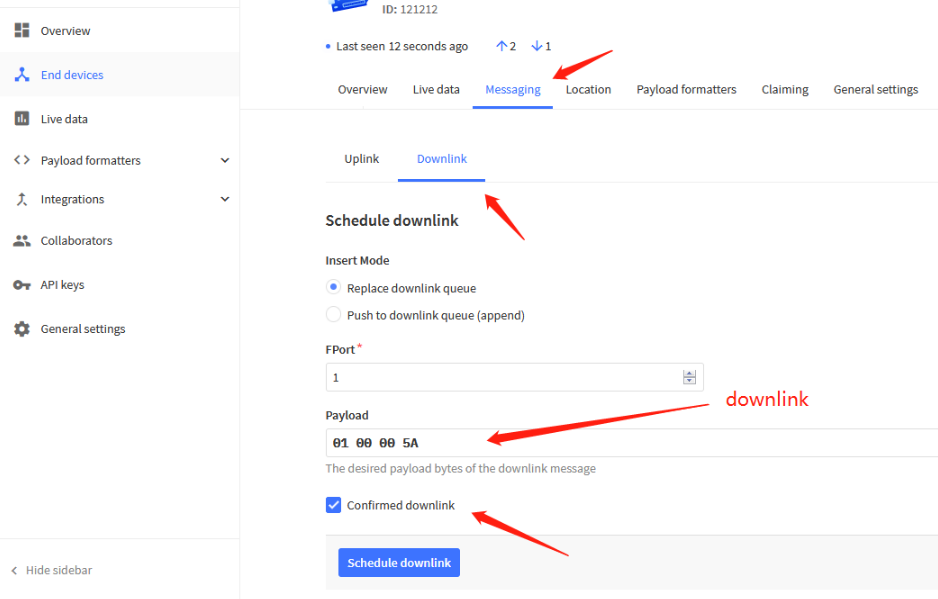
downlink
After sending, you can view it in live data.
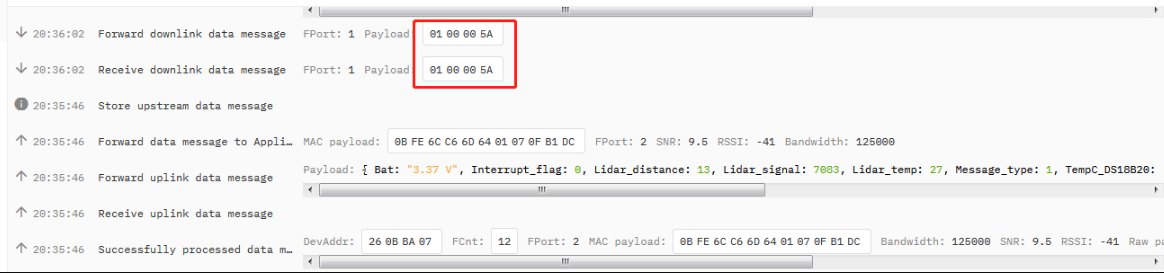
downlink
When downlink is successfully sent, the downlink information can be received on the serial port.
Note: If the downlink byte sent is longer, the number of bytes will be displayed.
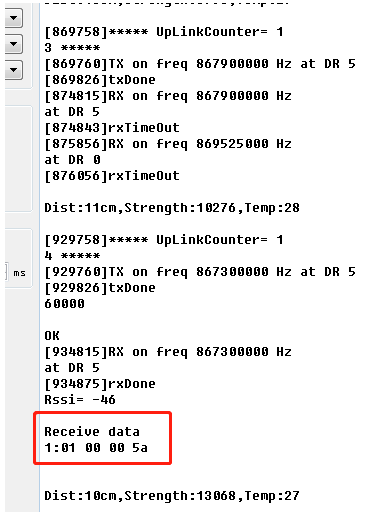
downlink
If you want to get a successful reply to send downlink in TTN v3. You need to set the response level.
If the equipment uses CLASS A. You can set AT+RPL=2 or send the downlink command: 2102
If the equipment uses CLASS C. You can set AT+RPL=4 or send the downlink command: 2104
When the device successfully receives the downlink, the server will receive a confirmation packet of 00.
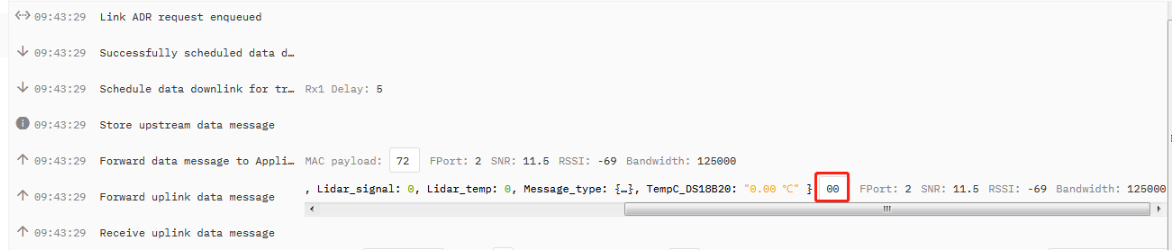
downlink
6. Route TTN data to Node-Red
Users can create an MQTT integration by following the steps described in "5.TTN V3 Integrated into MQTT Server"
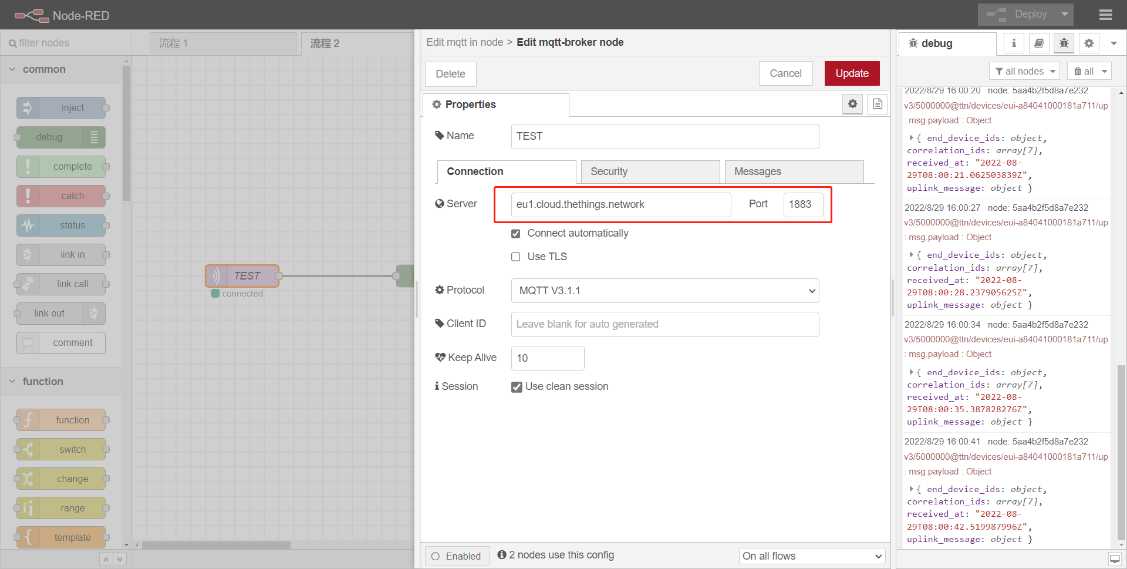
6.1 Edit mqtt-broker node
Users need to configure the TTN MQTT server address and port, Such as:
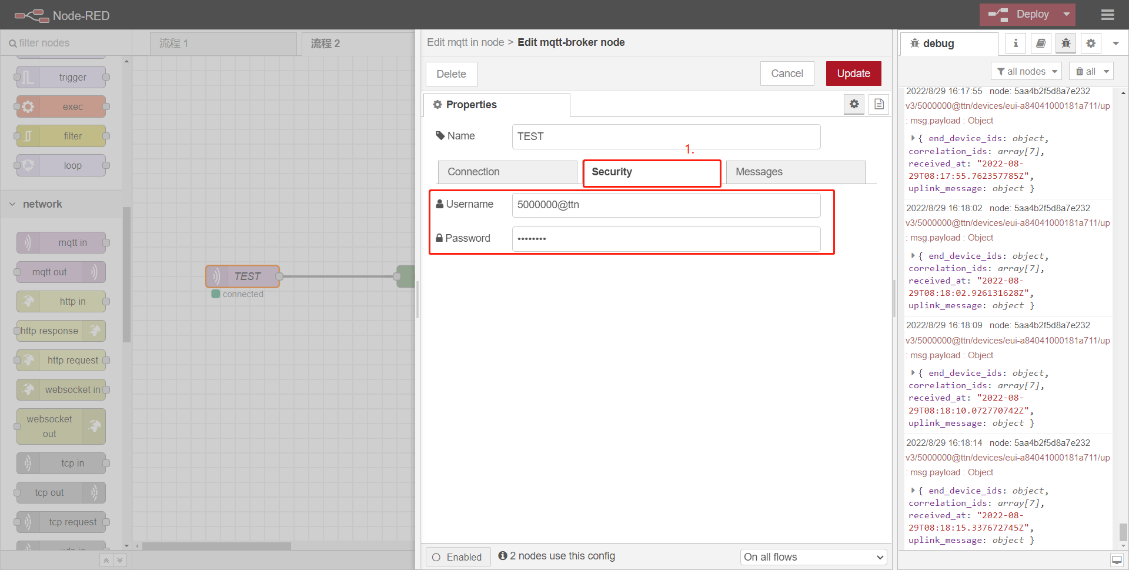
Enter Username and Password
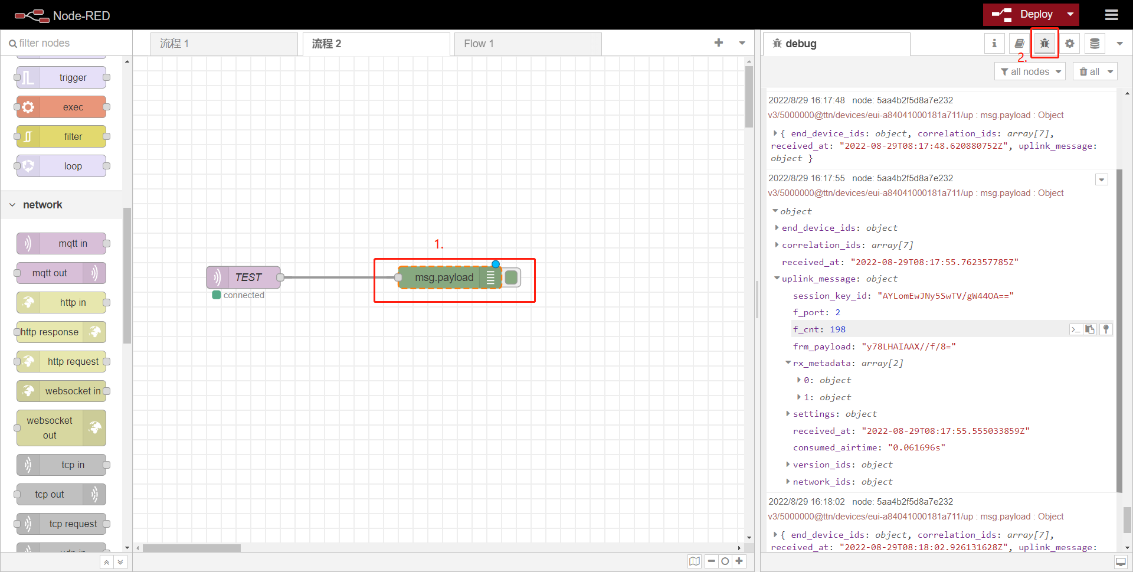
6.2 Debug
Users can check logs by adding debug.
6.3 Example: Use Local Server TTN and Node-Red in LPS8v2
LPS8v2 includes a local TTN Server and Node-Red. This example shows how to configure LHT65N to use with the local Node-Red server. This example assumes users already have:
- LHT65N register on LPS8v2 Built-In TTN server already
- The user is able to see the data on the built-in TTN server device page.
Below are the steps to plot the sensor data on LPS8v2 Node-Red.
6.3.1 Link Node-Red to Local TTN
Users can download the Node-Red decoder from this link and import it into the Node-Red platform: dragino-end-node-decoder/LHT65N.json at main · dragino/dragino-end-node-decoder (github.com)


6.3.2 Add input flow for device.
6.3.3 Check result.
7. Request Remote Support
These pages are useful to check what is wrong on the Join process. Below shows the four steps that we can check the Join Process.
If problem not solve, and you need dragino remote support, please follow to this document: TTN Support instruction If user has checked below steps and still can't solve the problem, please send us (support @ dragino.com) the screenshots for each step to check. They include:
- End node is connected to serial port to show the Join frequency and DR. (If possible)
- Gateway (from gateway UI) traffic to show the packet got from end node and receive from Server. (If possible)
- Gateway traffic (from server UI) to shows the data exchange between gateway and server. (Normally possible)
- End Node traffic (from server UI) to shows end node activity in server. (Normally possible)
- End Node Keys screen shot shows in end node and server. so we can check if the keys are correct. (In most case, we found keys doesn't match, especially APP EUI)
1. End Device Join Screen shot, we can check:
- If the device is sending join request to server?
- What frequency the device is sending?
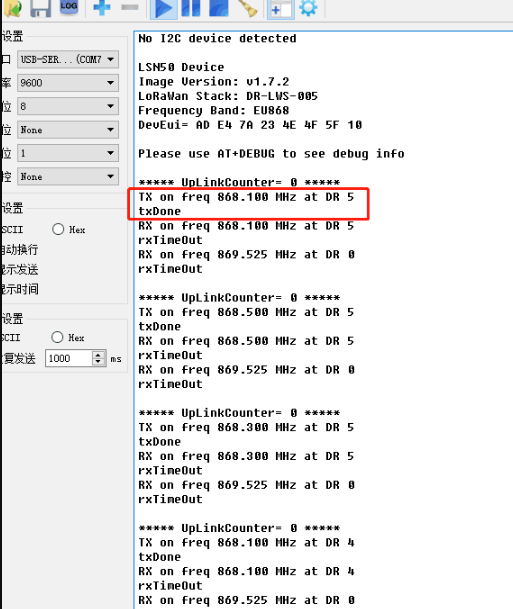
Console Output from End device to see the transmit frequency
User can run AT+CFG command to print configuration information.
- Is the device in OTAA mode or ABP mode? AT+NJM=1 (OTAA mode), AT+NJM=0 (ABP mode)
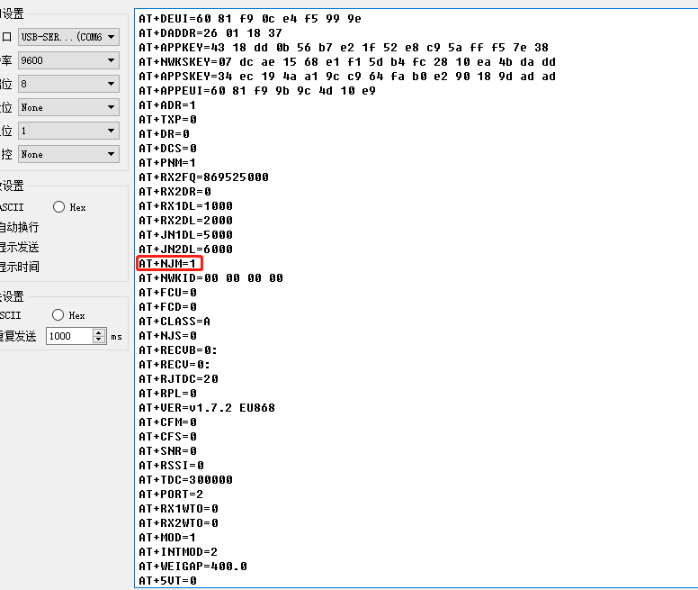
Console Output from End device to see the transmit frequency
2. Gateway packet traffic in gateway web or ssh. we can check:
If the gateway receive the Join request packet from sensor? (If this fail, check if the gateway and sensor works on the match frequency)
If the gateway gets the Join Accept message from server and transmit it via LoRa?
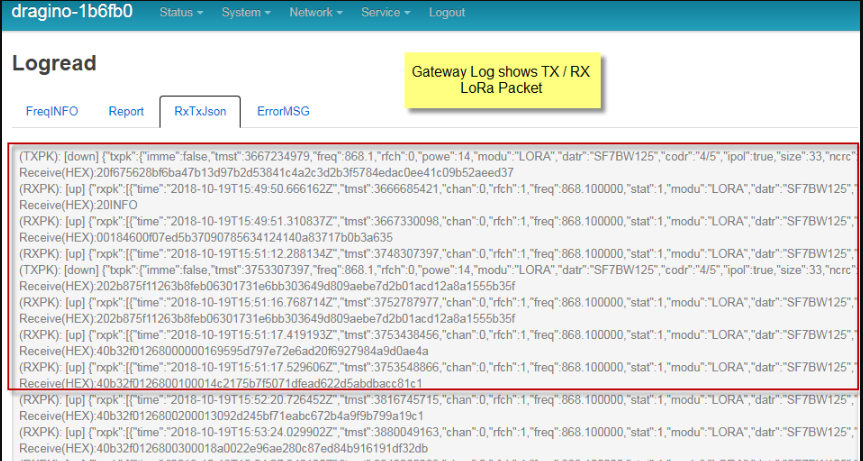
Console Output from Gateway to see packets between end node and server.
3. Gateway Traffic Page in LoRaWAN Server
If the Join Request packet arrive the gateway traffic in server? If not, check the internet connection and gateway LoRaWAN server settings.
If the server send back a Join Accept for the Join Request? if not, check if the keys from the device match the keys you put in the server, or try to choose a different server route for this end device.
If the Join Accept message are in correct frequency? If you set the server to use US915 band, and your end node and gateway is EU868, you will see the Join Accept message are in US915 band so no possible to Join success.
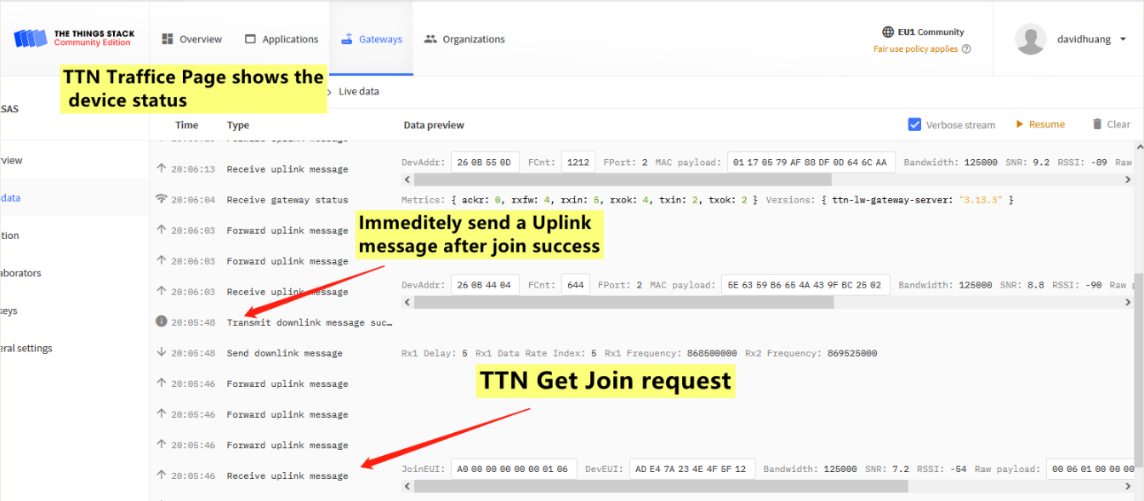
The Traffic for the End node in the server, use TTNv3 as example
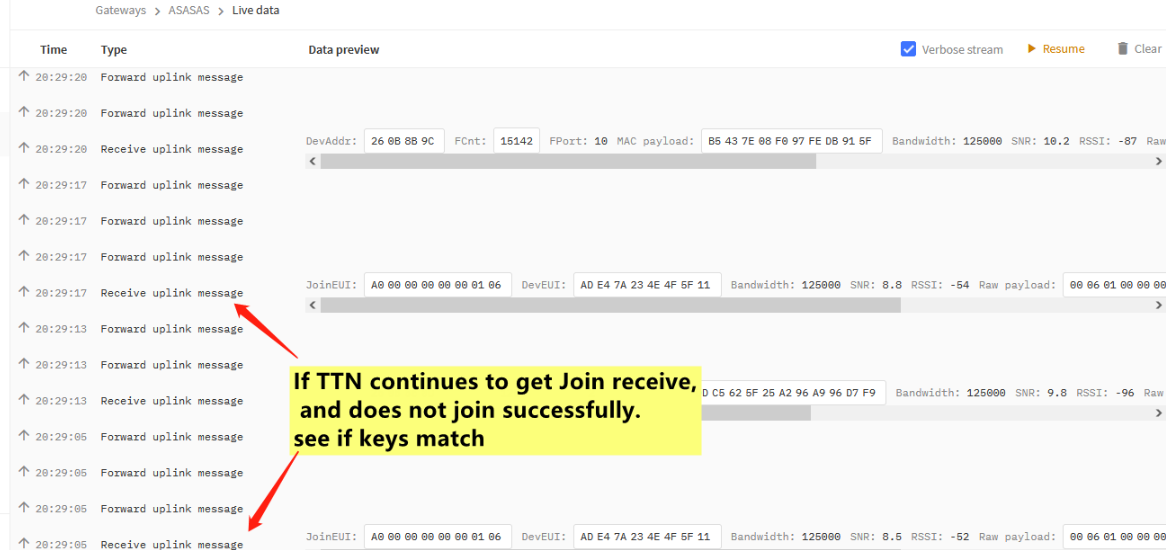
The Traffic for the End node in the server, use TTNv3 as example
4. Data Page in LoRaWAN server
If this data page shows the Join Request message from the end node? If not, most properly you have wrong settings in the keys. Keys in the server doesn't match the keys in End Node.
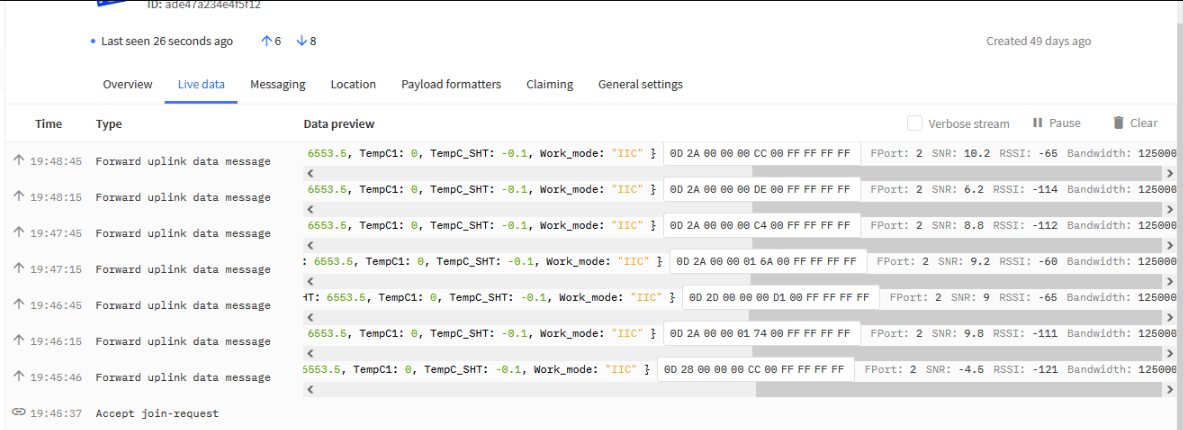
The data for the end device set in server

Check if OTAA Keys match the keys in device
